 全部商品分类
全部商品分类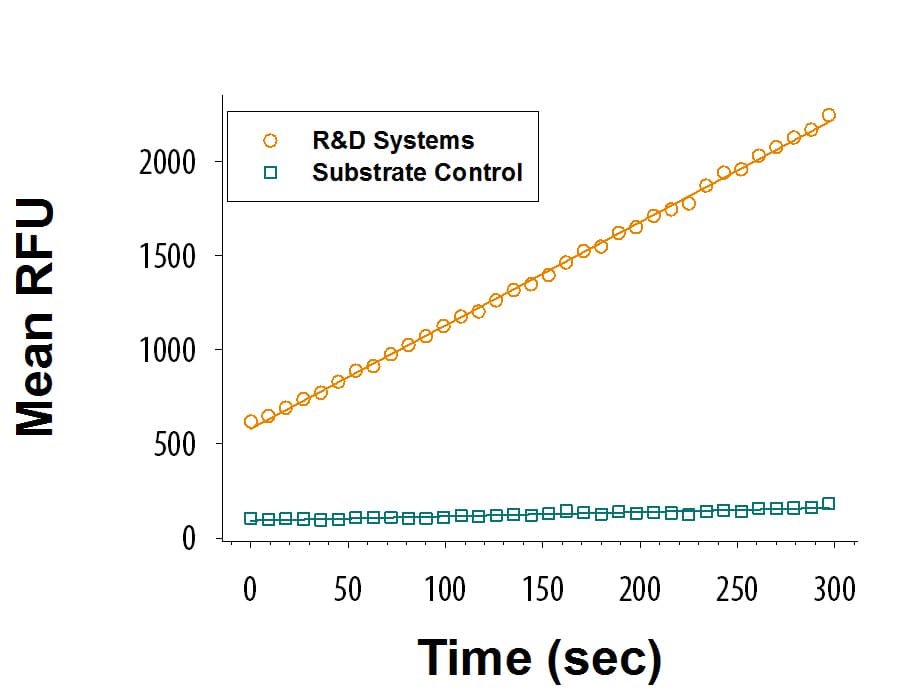

 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷



 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Scientific Data
 View Larger
View LargerRecombinant Human BCAT1 (Catalog # 9536-BA) is measured by its ability to convert leucine and alpha-ketoglutarate to alpha-ketoisocaproate and glutamate.
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
9536-BA
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris, NaCl, DTT and Glycerol. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Recombinant Human BCAT1 Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Lys2-Ser386
with an N-terminal Met and 6-His tag
Analysis

Background: BCAT1
Branched-chain-amino-acid aminotransferases (BCATs) are enzymes that catalyze the first reaction in the catabolism of the essential branched-chain amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and valine to their respective keto-acids while concurrently producing glutamate. BCATs belong to the class-IV pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent (PLP-dependent) aminotransferase family of enzymes (1). There are two BCAT isozymes in humans and mammals, a mitochondrial form known as BCATm or BCAT2 and a cytosolic form known as BCATc or BCAT1 that share 55% sequence identity. In humans and rodents, BCATm is found in most tissues whereas BCATc is almost exclusively present in the nervous system (2,3) where it is thought to play a role in glutamate neurotransmitter metabolism (1, 4). The 43 kDa human BCATc exists as an active homodimer and has a unique CXXC active site near the dimerization domain (4). BCATc can be regulated by redox and is implicated as a marker for oxidative stress (5,6) and linked to Alzheimers Disease and Dementia (7). BCATc has been shown to cause cell proliferation (8) and significant evidence has been found implicating BCATc in several types of cancer (8-10). In many reports, BCATc can be further used as a marker or for diagnostic purposes in cancers (11‑13).
- Hutson, S. (2001) Prog. Nucleic. Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 70:175
- Suryawan, A. et al. (1998) Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68:72.
- Hall, T.R. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:3092.
- Yennawar, N. H. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:39660.
- Coles, S.J. et al. (2012) Acta.Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 44:172.
- El Hindy, M. et al. (2014) Antioxid. Redox Signal 20:2497.
- Ashby, E.L. et al. (2017) Neurochem. Res. 42:306.
- Zhang, L. and J. Han (2017) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 486:224.
- Zhu, W. et al. (2017) Mol. Carcinog. 56:1570.
- Zheng, Y.H. et al. (2016) Liver Int. 36:1836.
- Young, G.P. et al. (2016) Cancer Med. 5:2763.
- Pedersen, S.K. (2015) BMC Cancer. 15:654.
- Diaz-Lagares, A. et al. (2016) Clin. Cancer Res. 22:3361.

参考图片
Recombinant Human BCAT1 (Catalog # 9536-BA) is measured byits ability to convert leucine and alpha-ketoglutarate to alpha-ketoisocaproateand glutamate.




