全部商品分类
全部商品分类

 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Scientific Data
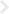
 View Larger
View LargerRecombinant human/mouse/rat BMP-2 (355-BM) induces alkaline phosphatase production in the ATDC5 mouse chondrogenic cell line. The ED50 for this effect is 40-200 ng/mL.
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
355-BM
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Glycine, Sucrose, Tween® 80 and Glutamic Acid with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100-200 μg/mL in sterile 4 mM HCl containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
355-BM/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Glycine, Sucrose, Tween® 80 and Glutamic Acid. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100-200 μg/mL in sterile 4 mM HCI. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat BMP-2 Protein Summary
Product Specifications
Gln283-Arg396
Background: BMP-2
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) is a member of the BMP subgroup of the TGF-beta superfamily. It plays a dominant role in embryonic dorsal-ventral patterning, organogenesis, limb bud formation, and bone formation and regeneration (1, 2). Human BMP‑2 is synthesized as a 396 amino acid (aa) preproprotein that contains a 23 aa signal sequence, a 259 aa prosegment, and a 114 aa mature region (3). Proteolytic removal of the propeptide enables mature BMP-2 to form active disulfide linked homodimers and heterodimers with BMP-7 (2). Mature monomeric BMP-2 is an 18 kDa glycosylated peptide with seven conserved cysteines that form a cystine knot structure (4). Mature human BMP-2 shares 100% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat BMP-2. It shares 85% aa sequence identity with human BMP-4 and less than 51% with other BMPs. BMP-2 signals through heterodimeric complexes composed of a type I receptor (Activin RI, BMPR‑IA, or BMPR‑IB) and a type II receptor (BMP RII or Activin RIIB) (2, 5). BMP-2 induces chondrocyte proliferation, endochondral bone formation, longitudinal bone growth, and bone and cartilage repair (6, 7). It induces ectopic bone formation or calcification by promoting osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation in mesenchymal cells, stem cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells (2, 8‑10). BMP-2/BMP-7 heterodimers are significantly more potent than BMP-2 homodimers at inducing bone formation in vivo (11). BMP-2 also promotes the maintenance and repair of colonic epithelium, suppresses neuronal dopamine synthesis and release, induces apoptosis in medulloblastoma cells, and is required for cardiac contractility (12‑15).
- Kishigami, S. and Y. Mishina (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:265.
- Chen, D. et al. (2004) Growth Factors 22:233.
- Wozney, J. et al. (1988) Science 242:1528.
- Sun, P.D. and D.R. Davies (1995) Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 24:269.
- Sebald, W. et al. (2004) Biol. Chem. 385:697.
- De Luca, F. et al. (2001) Endocrinology 142:430.
- Davidson, E.N.B., et al. (2007) Arthritis Res. Ther. 9:R102.
- Ryoo, H.-M. et al. (2006) Gene 366:51.
- Kramer, J. et al. (2000) Mech. Dev. 92:193.
- Li, X. et al. (2008) Atherosclerosis January 5 epub.
- Zhu, W. et al. (2004) J. Bone Miner. Res. 19:2021.
- Peiris, D. et al. (2007) Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 292:G753.
- Kano, Y. et al. (2005) Endocrinology 146:5332.
- Hallahan, A.R. et al. (2003) Nat. Med. 9:1033.
- Wang, Y.-X. et al. (2007) Cardiovasc. Res. 74:290.