全部商品分类
全部商品分类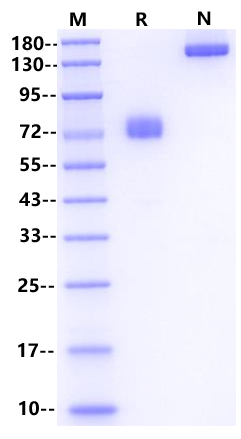



 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询73-88 kDa(Reducing)
Pro20-Lys291, with C-terminal human IgG Fc

73-88 kDa(Reducing)








1μg (R: reducing conditions, N: non-reducing conditions)
"}]
CD19 is a 95 kDa type-I transmembrane glycoprotein and a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is extensively expressed on B cells during most stages of B-cell differentiation, with expression levels decreasing as B cells terminally differentiate into plasma cells. Genetic mapping places CD19 at the 16p11.2 locus on chromosome 16, where it encodes a 540 amino acid protein. This protein features two extracellular C-type IgSF domains and a large cytoplasmic tail of approximately 240 residues, which shows significant conservation between mice and humans.
CD19 functions as a signal-amplifying coreceptor, with its expression limited to B cells and follicular dendritic cells. It is part of a multimolecular complex on the B cell surface that includes CD21 (complement receptor type 2, CR2), the tetraspanin CD81, and CD225. Through its interaction with CD21, CD19 acts as a signal transducing component for antigens bound by complement. The co-ligation of the B cell receptor (BCR) and the CD19/CD21 complex significantly lowers the activation threshold of B cells by approximately two orders of magnitude.
Recognizing its role in B cell biology, CD19 has emerged as a potential target for monoclonal antibody therapy. Early data have shown its potential in B-cell depletion, presenting an attractive treatment option for autoimmune diseases and malignant B-cell lymphomas. The rationale for CD19 as a target for immunotherapy includes: (1) its expression on the majority of B-cell malignancies; (2) its early expression in the B-cell lineage, preceding even CD20; (3) its efficient internalization in lymphoma tumor models; and (4) its potential involvement in the development of B-cell cancers.

Reconstitute at 0.1-1mg/mL according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.

· 12 months from date of receipt, lyophilized powder stored at -20 to -80℃.
· 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
· 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
· Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
1. Zola H, et al. (2007) CD molecules 2006-human cell differentiation molecules. J Immunol Methods. 318 (1-2): 1-5.
2. Ho IC, et al. (2009) GATA3 and the T-cell lineage: essential functions before and after T-helper-2-cell differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol. 9 (2): 125-35.
3. Matesanz-Isabel J, et al. (2011) New B-cell CD molecules. Immunology Letters.134 (2): 104-12.
4. Carter RH, et al. (1992) CD19: lowering the threshold for antigen receptor stimulation of B lymphocytes. Science. 256 (5053): 105-7.

参考图片
1μg (R: reducing conditions, N: non-reducing conditions)
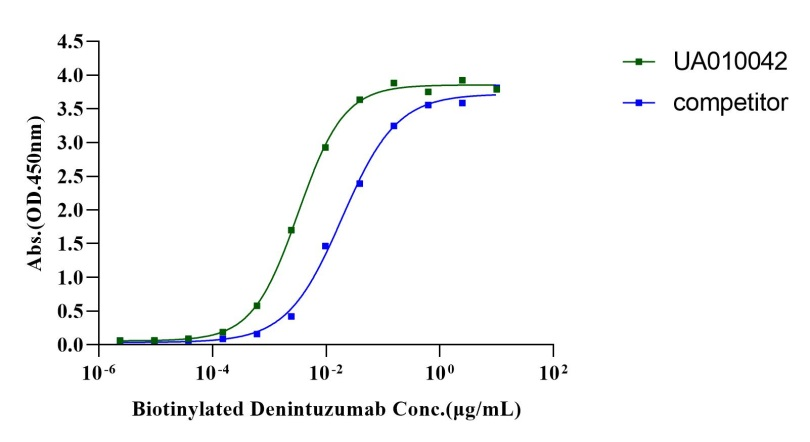
Immobilized CD19 Fc Chimera Protein, Human (Cat. No. UA010412)at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind Biotinylated Denintuzumab with EC50 of 2.86-3.66ng/mL.
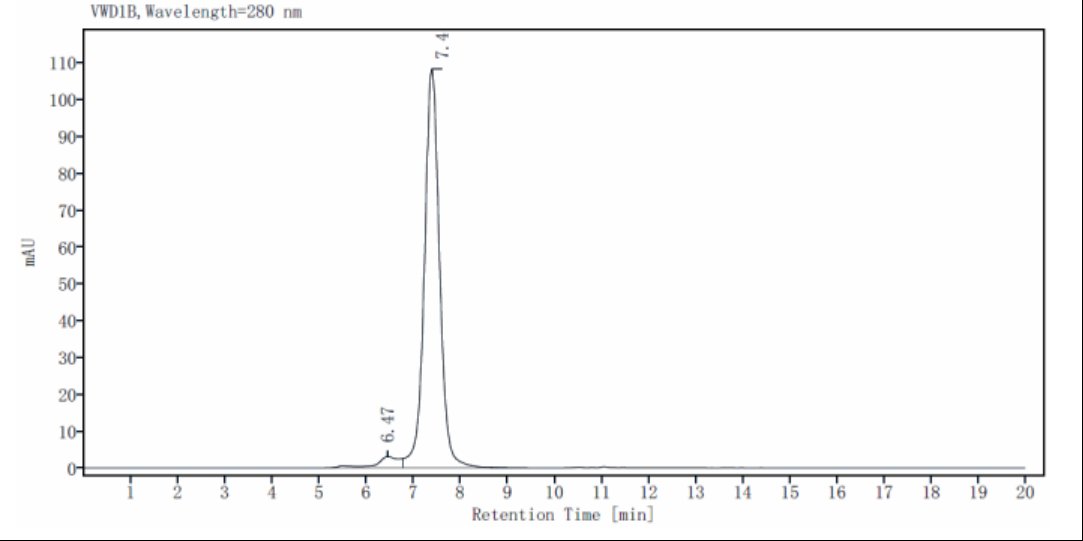
The purity of CD19 Fc Chimera Protein, Human is more than 95% determined by SEC-HPLC.
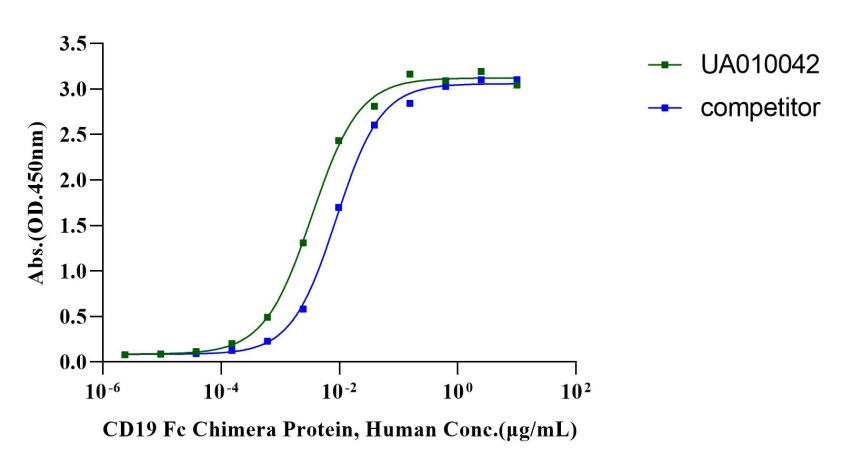
Immobilized FMC63 at 1.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind CD19 Fc Chimera Protein, Human (Cat. No. UA010412) with EC50 of 2.89-4.07ng/mL, bind CD19 Fc Chimera Protein, Human (competitor) with EC50 of 7.77-10.10ng/mL.