 全部商品分类
全部商品分类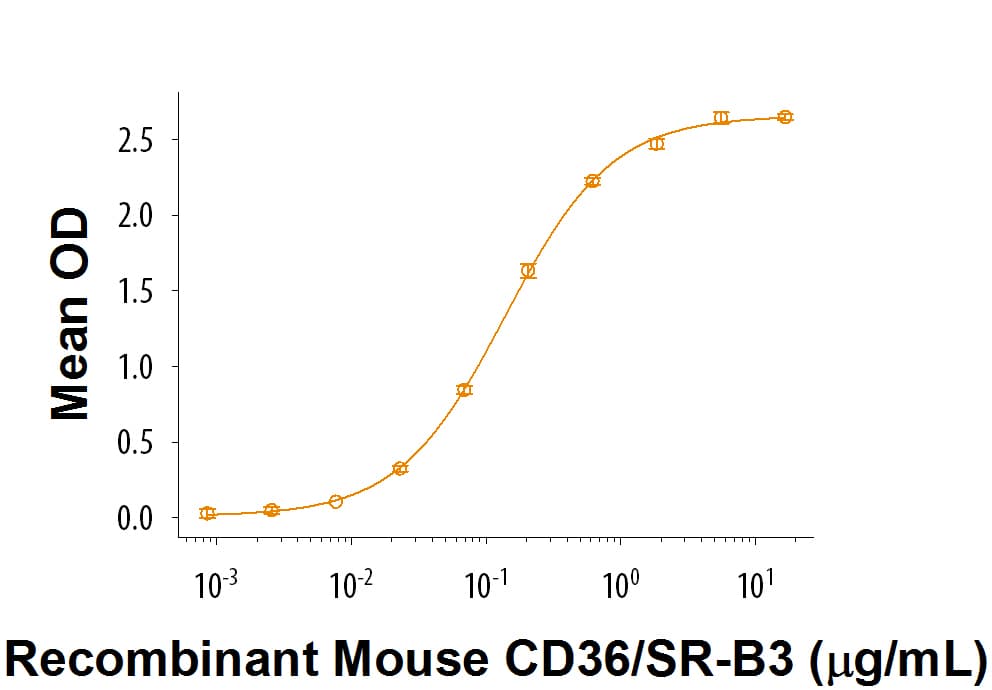

 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Scientific Data
 View Larger
View LargerRecombinant Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 2519-CD) is used at 1 µg/mL, Recombinant Human Thrombospondin-2 (Catalog # 1635-T2) binds with an ED50 of 0.06-0.6 µg/mL.
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
2519-CD
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Recombinant Mouse CD36/SR-B3 Fc Chimera Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
| Mouse CD36 (Gly30-Lys439) Accession # Q3UAI3 | IEGRMD | Human IgG1 (Pro100-Lys330) |
| N-terminus | C-terminus | |
Analysis

Background: CD36/SR-B3
CD36 (alternatively known as platelet membrane glycoprotein IV (GPIV), thrombospondin receptor, fatty acid translocase (FAT), and scavenger receptor class B, member 3 (SR-B3)) is an 88 kDa, integral membrane glycoprotein that belongs to the class B scavenger receptor family (1, 2). The molecule is described as being ditopic, with two transmembrane segments connected by an extracellular loop (3). Mouse CD36 is synthesized as a 472 amino acid (aa) protein that contains a 6 aa N-terminal cytoplasmic domain, a 22 aa N-terminal transmembrane segment, a 420 aa extracellular “loop”, a 22 aa C-terminal transmembrane segment, and a 9 aa C-terminal cytoplasmic tail (4). Both cytoplasmic tails are palmitoylated, with the C-terminal tail involved in oxidized LDL binding (5, 6). With respect to the extracellular loop, the N-terminal region is believed to bind both thrombospondin-1 and Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes. Other ligands for CD36 include long-chain fatty acids, collagen, phospholipids and apoptotic cells (1). The extracellular loop of mouse CD36 is 94%, 92%, 84% and 84% aa identical to the extracellular loops of rat, hamster, human and bovine CD36, respectively. Cells known to express CD36 include capillary endothelium, adipocytes, skeletal muscle cells, intestinal epithelium, smooth muscle cells and hematopoietic cells such as RBC’s, platelets and monocytes (1). On the surface of cells, CD36 is suggested to exist as a dimer in response to ligation (7). CD36 is reported to regulate fatty uptake, act as an angiogenic with TSP-1, and participate in the clearance of apoptotic phagocytes (1, 8).
- Febbraio, M. et al. (2001) J. Clin. Invest. 108:795.
- Silverstein, R.L. and M. Febbraio (2000) Curr. Opin. Lipid. 11:483.
- Gruarin, P. et al. (2000) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 275:446.
- Endemann, G. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:11811.
- Malaud, E. et al. (2002) Biochem. J. 364:507.
- Tao, N. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:22315.
- Daviet, L. et al. (1997) Thromb. Haemost. 78:897.
- Simantov, R. and R.L. Silverstein (2003) Front. Biosci. 8:s874.






