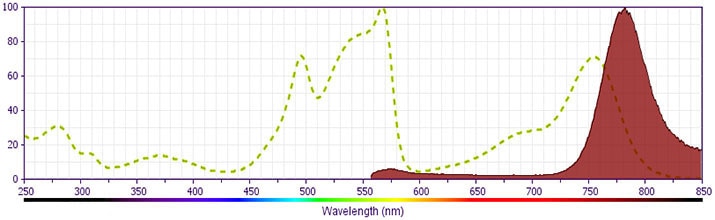
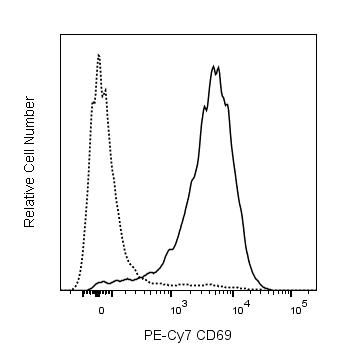
研发参考(16)
1. Bendelac A, Matzinger P, Seder RA, Paul WE, Schwartz RH. Activation events during thymic selection. J Exp Med. 1992; 175(3):731-742. (Biology).
2. Brandle D, Muller S, Muller C, Hengartner H, Pircher H. Regulation of RAG-1 and CD69 expression in the thymus during positive and negative selection. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(1):145-151. (Biology).
3. Gabor MJ, Godfrey DI, Scollay R. Recent thymic emigrants are distinct from most medullary thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1997; 27(8):2010-2050. (Biology).
4. Karlhofer FM, Yokoyama WM. Stimulation of murine natural killer (NK) cells by a monoclonal antibody specific for the NK1.1 antigen. IL-2-activated NK cells possess additional specific stimulation pathways. J Immunol. 1991; 146(10):3662-3673. (Clone-specific: Cytotoxicity).
5. Keefe R, Dave V, Allman D, Wiest D, Kappes DJ. Regulation of lineage commitment distinct from positive selection. Science. 1999; 286(5442):1149-1153. (Biology).
6. Lauzurica P, Sancho D, Torres M, et al. Phenotypic and functional characteristics of hematopoietic cell lineages in CD69-deficient mice. Blood. 2000; 95(7):2312-2320. (Biology).
7. Merkenschlager M, Graf D, Lovatt M, Bommhardt U, Zamoyska R, Fisher AG. How many thymocytes audition for selection. J Exp Med. 1997; 186(7):1149-1158. (Biology).
8. Nishimura T, Kitamura H, Iwakabe K, et al. The interface between innate and acquired immunity: glycolipid antigen presentation by CD1d-expressing dendritic cells to NKT cells induces the differentiation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 2000; 12(7):987-994. (Biology).
9. Punt JA, Suzuki H, Granger LG, Sharrow SO, Singer A. Lineage commitment in the thymus: only the most differentiated (TCRhibcl-2hi) subset of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes has selectively terminated CD4 or CD8 synthesis. J Exp Med. 1996; 184(6):2091-2099. (Biology).
10. Roederer M, Kantor AB, Parks DR, Herzenberg LA. Cy7PE and Cy7APC: bright new probes for immunofluorescence. Cytometry. 1996; 24(3):191-197. (Biology).
11. Sobel ES, Yokoyama WM, Shevach EM, Eisenberg RA, Cohen PL. Aberrant expression of the very early activation antigen on MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993; 150(2):673-682. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation).
12. Wilkinson RW, Anderson G, Owen JJ, Jenkinson EJ. Positive selection of thymocytes involves sustained interactions with the thymic microenvironment. J Immunol. 1995; 155(11):5234-5240. (Biology).
13. Yokoyama WM, Koning F, Kehn PJ, et al. Characterization of a cell surface-expressed disulfide-linked dimer involved in murine T cell activation. J Immunol. 1988; 141(2):369-376. (Immunogen: (Co)-stimulation).
14. Yokoyama WM, Maxfield SR, Shevach EM. Very early (VEA) and very late (VLA) activation antigens have distinct functions in T lymphocyte activation. Immunol Rev. 1989; 109:153-176. (Biology).
15. Ziegler SF, Levin SD, Johnson L, et al. The mouse CD69 gene. Structure, expression, and mapping to the NK gene complex. J Immunol. 1994; 152(3):1228-1236. (Biology).
16. Ziegler SF, Ramsdell F, Alderson MR. The activation antigen CD69. Stem Cells. 1994; 12(5):456-465. (Biology).

 全部商品分类
全部商品分类



 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询