 全部商品分类
全部商品分类

1/2

品牌: BD Pharmingen
 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询反应种属:
Mouse (QC Testing)
来源宿主:
Armenian Hamster IgG1, λ3
产品介绍
产品使用步骤推荐 产品介绍
产品信息
荧光素标记
抗原名称
CD69

宿主
Armenian Hamster IgG1, λ3

免疫原
Mouse Dendritic Epidermal T Cell Line Y245

简单描述
The H1.2F3 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD69 (Very Early Activation antigen), an 85 kDa disulfide-linked homodimer of differentially glycosylated subunits. CD69 is a C-type lectin, most closely related to the NKR-P1 and Ly-49 NK cell-activation molecules. Its expression is rapidly induced upon activation of lymphocytes (T, B, NK, and NK-T cells), neutrophils, and macrophages. CD69 is expressed also on thymocytes that are undergoing positive selection; its role in that process is unclear. H1.2F3 mAb augments PMA-induced T-cell stimulation and IFN-γ-induced macrophage stimulation. IL-2-activated NK cells express CD69, and H1.2F3 mAb induces redirected lysis of FcR-bearing target cells by NK cells.
This antibody is conjugated to BD Horizon™ PE-CF594, which has been developed exclusively by BD Biosciences as a better alternative to PE-Texas Red®. PE-CF594 excites and emits at similar wavelengths to PE-Texas Red® yet exhibits improved brightness and spectral characteristics. Due to PE having maximal absorption peaks at 496 nm and 564 nm, PE-CF594 can be excited by the blue (488-nm), green (532-nm) and yellow-green (561-nm) lasers and can be detected with the same filter set as PE-Texas Red® (eg 610/20-nm filter).

商品描述
H1.2F3
The H1.2F3 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD69 (Very Early Activation antigen), an 85 kDa disulfide-linked homodimer of differentially glycosylated subunits. CD69 is a C-type lectin, most closely related to the NKR-P1 and Ly-49 NK cell-activation molecules. Its expression is rapidly induced upon activation of lymphocytes (T, B, NK, and NK-T cells), neutrophils, and macrophages. CD69 is expressed also on thymocytes that are undergoing positive selection; its role in that process is unclear. H1.2F3 mAb augments PMA-induced T-cell stimulation and IFN-γ-induced macrophage stimulation. IL-2-activated NK cells express CD69, and H1.2F3 mAb induces redirected lysis of FcR-bearing target cells by NK cells.
This antibody is conjugated to BD Horizon™ PE-CF594, which has been developed exclusively by BD Biosciences as a better alternative to PE-Texas Red®. PE-CF594 excites and emits at similar wavelengths to PE-Texas Red® yet exhibits improved brightness and spectral characteristics. Due to PE having maximal absorption peaks at 496 nm and 564 nm, PE-CF594 can be excited by the blue (488-nm), green (532-nm) and yellow-green (561-nm) lasers and can be detected with the same filter set as PE-Texas Red® (eg 610/20-nm filter).

同种型
Armenian Hamster IgG1, λ3

克隆号
克隆 H1.2F3 (RUO)

浓度
0.2 mg/ml

产品详情
PE-CF594
BD Horizon™ PE-CF594 dye is a part of the BD PE family of dyes. This tandem fluorochrome is comprised of a R-Phycoerythrin (PE) donor that has excitation maxima (Ex Max) of 496-nm and 566-nm and an acceptor dye with an emission maximum (Em Max) at 615-nm. PE-CF594, driven by BD innovation, is designed to be excited by the blue (488-nm), Green (532-nm) and yellow-green (561-nm) lasers and detected using an optical filter centered near 615 nm (e.g., a 610/20-nm bandpass filter). The donor dye can be excited by the Blue (488-nm), Green (532-nm) and yellow-green (561-nm) lasers and the acceptor dye can be excited by the green (532-nm) laser resulting in cross-laser excitation and fluorescence spillover. Please ensure that your instrument’s configurations (lasers and optical filters) are appropriate for this dye.
PE-CF594
Yellow-Green 488 nm, 532 nm, 561 nm
496 nm, 566 nm
615 nm
应用
实验应用
Flow cytometry (Routinely Tested)

反应种属
Mouse (QC Testing)

目标/特异性
CD69

背景
别名
VEA; Very Early Activation Antigen; AIM; Activation Induced Molecule

制备和贮存
存储溶液
Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA, protein stabilizer, and ≤0.09% sodium azide.

保存方式
Aqueous buffered solution containing BSA, protein stabilizer, and ≤0.09% sodium azide.
文献
文献
研发参考(16)
1. Bendelac A, Matzinger P, Seder RA, Paul WE, Schwartz RH. Activation events during thymic selection. J Exp Med. 1992; 175(3):731-742. (Biology).
2. Brandle D, Muller S, Muller C, Hengartner H, Pircher H. Regulation of RAG-1 and CD69 expression in the thymus during positive and negative selection. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(1):145-151. (Biology).
3. Gabor MJ, Godfrey DI, Scollay R. Recent thymic emigrants are distinct from most medullary thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1997; 27(8):2010-2050. (Biology).
4. Karlhofer FM, Yokoyama WM. Stimulation of murine natural killer (NK) cells by a monoclonal antibody specific for the NK1.1 antigen. IL-2-activated NK cells possess additional specific stimulation pathways. J Immunol. 1991; 146(10):3662-3673. (Clone-specific: Induction).
5. Keefe R, Dave V, Allman D, Wiest D, Kappes DJ. Regulation of lineage commitment distinct from positive selection. Science. 1999; 286(5442):1149-1153. (Biology).
6. Lauzurica P, Sancho D, Torres M, et al. Phenotypic and functional characteristics of hematopoietic cell lineages in CD69-deficient mice. Blood. 2000; 95(7):2312-2320. (Biology).
7. Marzio R, Jirillo E, Ransijn A, Mauel J, Corradin SB. Expression and function of the early activation antigen CD69 in murine macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1997; 62(3):349-355. (Clone-specific: Stimulation).
8. Merkenschlager M, Graf D, Lovatt M, Bommhardt U, Zamoyska R, Fisher AG. How many thymocytes audition for selection. J Exp Med. 1997; 186(7):1149-1158. (Biology).
9. Nishimura T, Kitamura H, Iwakabe K, et al. The interface between innate and acquired immunity: glycolipid antigen presentation by CD1d-expressing dendritic cells to NKT cells induces the differentiation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 2000; 12(7):987-994. (Biology).
10. Punt JA, Suzuki H, Granger LG, Sharrow SO, Singer A. Lineage commitment in the thymus: only the most differentiated (TCRhibcl-2hi) subset of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes has selectively terminated CD4 or CD8 synthesis. J Exp Med. 1996; 184(6):2091-2099. (Biology).
11. Sobel ES, Yokoyama WM, Shevach EM, Eisenberg RA, Cohen PL. Aberrant expression of the very early activation antigen on MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993; 150(2):673-682. (Clone-specific: Stimulation).
12. Wilkinson RW, Anderson G, Owen JJ, Jenkinson EJ. Positive selection of thymocytes involves sustained interactions with the thymic microenvironment. J Immunol. 1995; 155(11):5234-5240. (Biology).
13. Yokoyama WM, Koning F, Kehn PJ, et al. Characterization of a cell surface-expressed disulfide-linked dimer involved in murine T cell activation. J Immunol. 1988; 141(2):369-376. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry, Stimulation).
14. Yokoyama WM, Maxfield SR, Shevach EM. Very early (VEA) and very late (VLA) activation antigens have distinct functions in T lymphocyte activation. Immunol Rev. 1989; 109:153-176. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Stimulation).
15. Ziegler SF, Levin SD, Johnson L, et al. The mouse CD69 gene. Structure, expression, and mapping to the NK gene complex. J Immunol. 1994; 152(3):1228-1236. (Biology).
16. Ziegler SF, Ramsdell F, Alderson MR. The activation antigen CD69. Stem Cells. 1994; 12(5):456-465. (Biology).

数据库链接
Entrez-Gene ID
12515

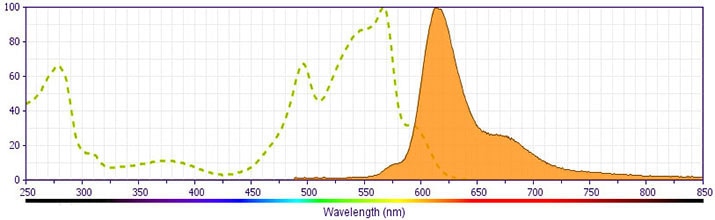
参考图片
Flow cytometric analysis of CD69 expression on stimulated mouse splenocytes. BALB/c splenocytes were stimulated for 5 hours at 37°C with 10 ng/mL Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate (PMA; Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. P-8139) and stained either with BD Horizon™ PE-CF594 Hamster IgG1, λ1 Isotype Control (Cat. No.562521; dashed line histogram) or with the BD Horizon™ PE-CF594 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD69 antibody (Cat. No. 562455; solid line histogram). The fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable cells. Flow cytometry was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.
声明 :本官网所有报价均为常温或者蓝冰运输价格,如有产品需要干冰运输,需另外加收干冰运输费。





