 全部商品分类
全部商品分类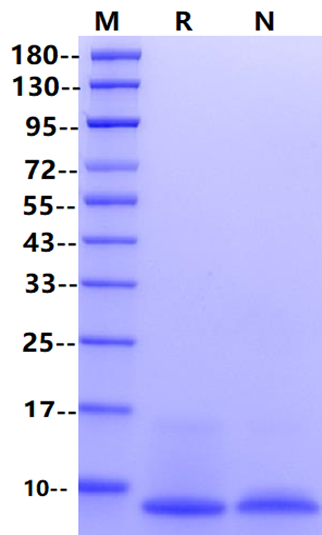













Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) belongs to the family of insulin-like growth factors that are structurally homologous to proinsulin. Mature IGFs are generated by proteolytic processing of inactive precursor protein containing N-terminal and C-terminal propeptide regions. IGF-I is produced primarily by the liver as an endocrine hormone as well as in target tissues in a paracrine/autocrine fashion. The production of IGF-I is stimulated by growth hormone (GH) and can be retarded by undernutrition, growth hormone insensitivity, lack of growth hormone receptors, or failures of the downstream signaling pathway post GH receptor including SHP2 and STAT5B. IGF-I binds IGF-1R, IGF-2R, and the insulin receptor and plays a key role in cell cycle progression, cell proliferation and tumor progression. Accession#: P08025 https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/ P08025 /entry


· 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
· 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
· Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
1. Bartlett WP, Li XS, Williams M. 1992. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 12: 285-91.

参考图片
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
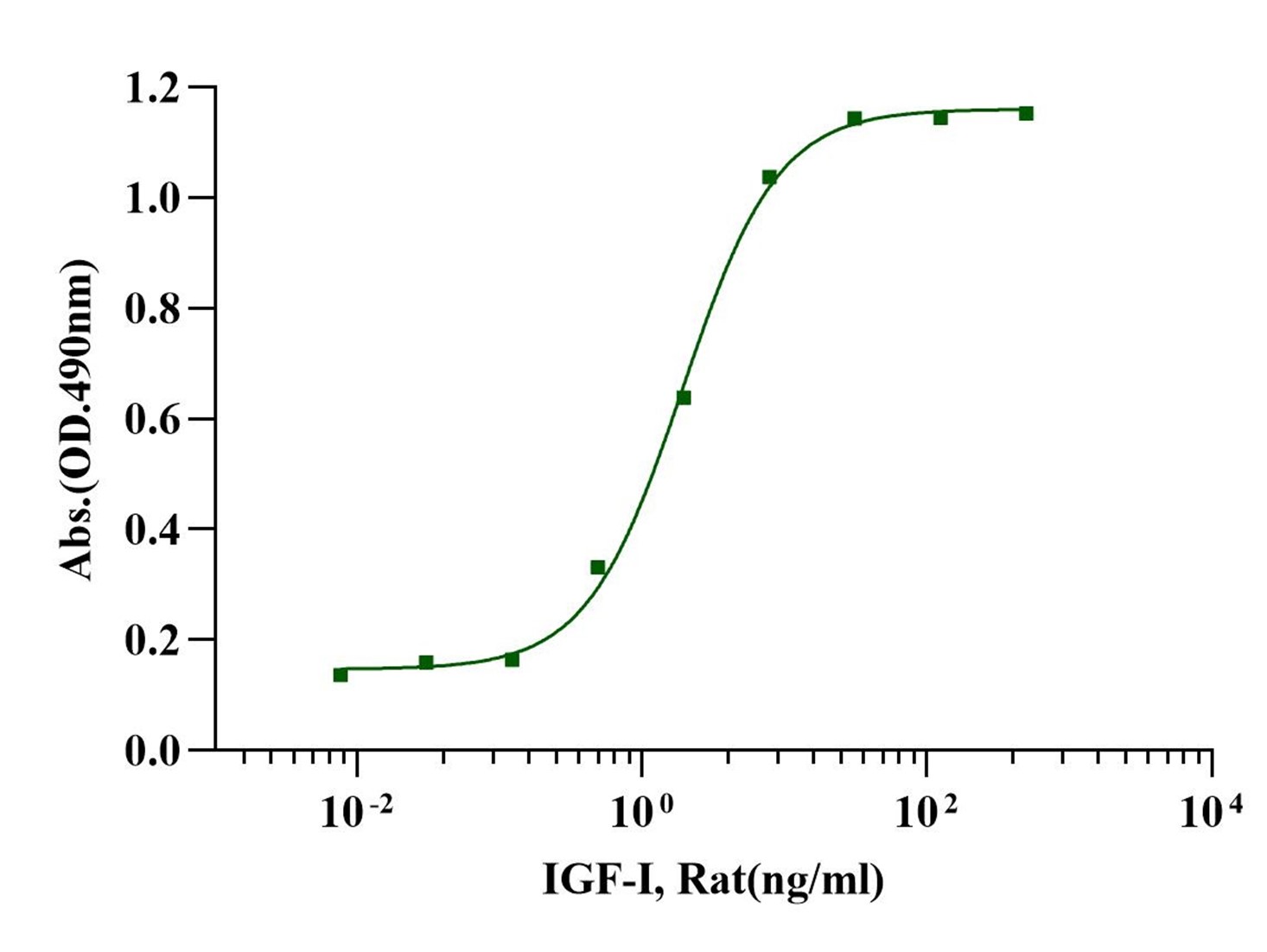
Measured in a serum-free cell proliferation assay using MCF‑7 human breast cancer cells. The EC50 for this effect is less than 2ng/ml.





 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷




