全部商品分类
全部商品分类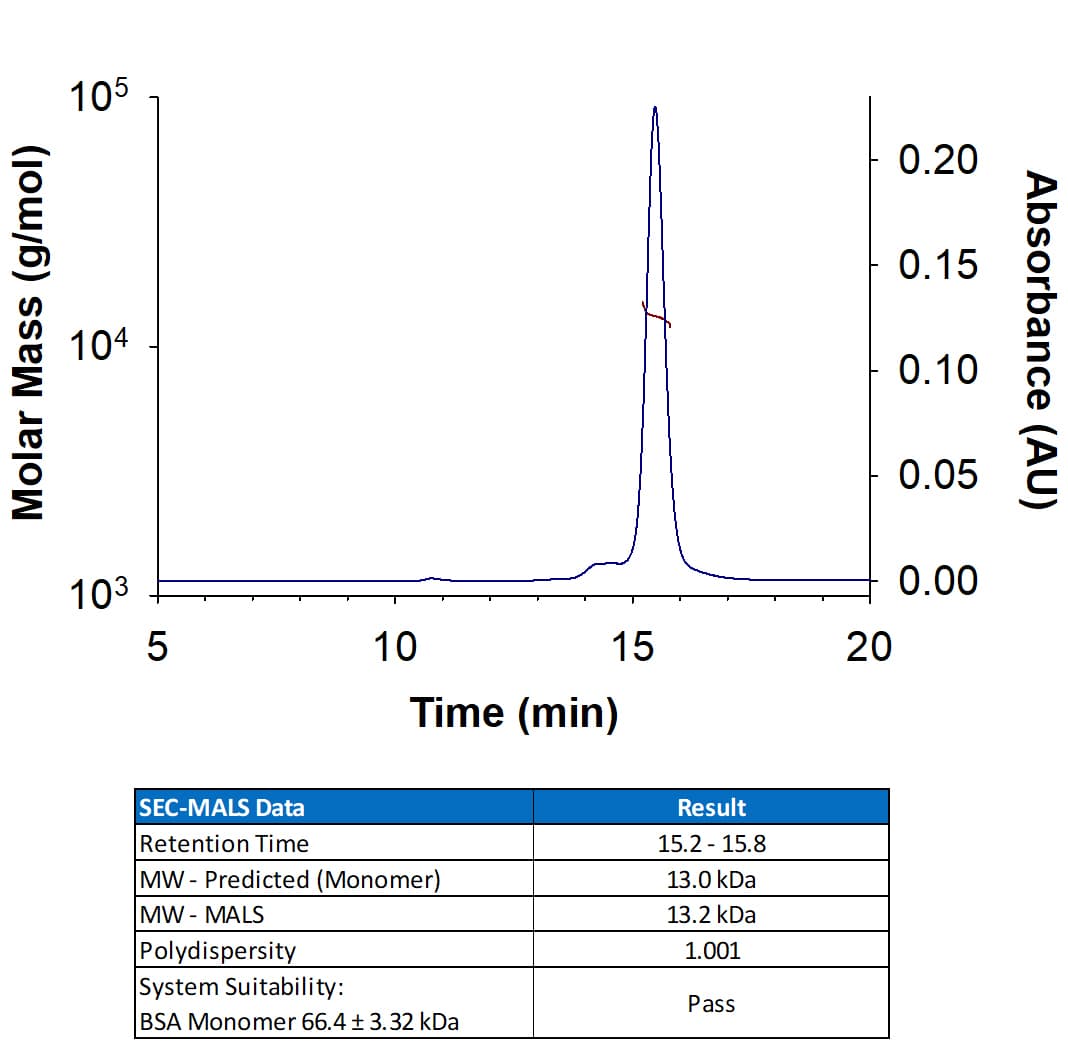



 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Scientific Data
 View Larger
View LargerRecombinant Human IL-15 (Catalog # BT-015) has a molecular weight (MW) of 13.2 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a monomer.
 View Larger
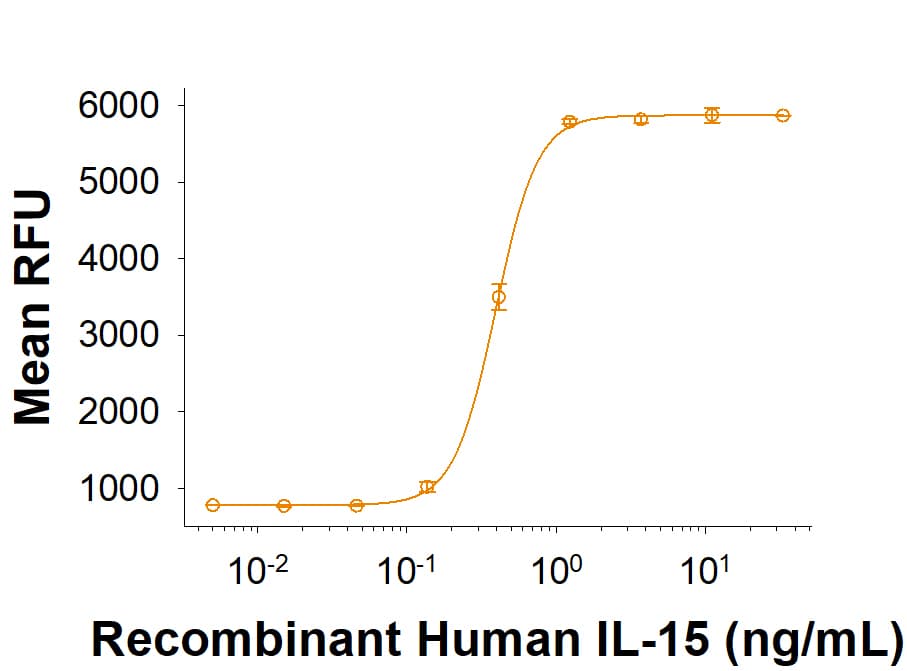
View LargerRecombinant Human IL-15 (Catalog # BT-015) stimulates cell proliferation in the MO7e human megakaryocytic leukemic cell line. The ED50 for this effect is 0.300-2.60 ng/mL.
 View Larger
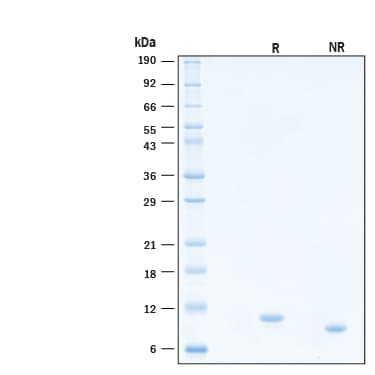
View Larger2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human IL‑15 Protein (Catalog # BT-015) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 9 kDa.
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
BT-015
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100-500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Recombinant Human IL-15 Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Asn49-Ser162
Analysis

Background: IL-15
Interleukin 15 (IL-15) is a widely expressed 14 kDa cytokine that is structurally and functionally related to IL-2 and plays an important role in many immunological diseases (1, 2). Mature human IL-15 shares 70% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat IL-15. Alternative splicing generates isoforms of IL-15 with either a long or short signal peptide (LSP or SSP), and the SSP isoform is retained intracellularly (3). IL-15 binds with high affinity to IL-15 R alpha (4). It binds with lower affinity to a complex of IL-2 R beta and the common gamma chain ( gamma c) which are also subunits of the IL-2 receptor complex (5). IL-15 associates with IL-15 R alpha in the endoplasmic reticulum, and this complex is expressed on the cell surface (6).
The dominant mechanism of IL-15 action is known as transpresentation in which IL-15 and IL-15 R alpha are coordinately expressed on the surface of one cell and interact with complexes of IL-2 R beta / gamma c on adjacent cells (7). This enables cells to respond to IL-15 even if they do not express IL-15 R alpha (6). In human and mouse, soluble IL-15-binding forms of IL-15 R alpha can be generated by proteolytic shedding and bind up nearly all the IL-15 in circulation (8-10). Soluble IL-15 R alpha functions as an inhibitor that limits IL-15 action (4, 9). Ligation of membrane-associated IL-15/IL-15 R alpha complexes also induces reverse signaling that promotes activation of the IL-15/IL-15 R alpha expressing cells (11). IL-15 induces or enhances the differentiation, maintenance, or activation of multiple T cell subsets including NK, NKT, Th17, Treg, and CD8+ memory cells (12 - 16). An important component of these functions is the ability of IL‑15 to induce dendritic cell differentiation and inflammatory activation (11, 14). IL-15 exhibits anti-tumor activity independent of its actions on NK cells or CD8+ T cells (17). It also inhibits the deposition of lipid in adipocytes, and its circulating levels are decreased in obesity (18).
Immunotherapy treatment with recombinant IL-15 has the advantage of not stimulating Treg cells like IL-2 does but has the drawback of associated toxicity at higher doses. This has led to increased investigation on mitigating IL-15 toxicity and combination immunotherapy approaches using immune checkpoint inhibitors (19, 20). Preclinical and early clinical studies have shown the potential of also using IL-15 in combination with cancer vaccines to improve their anti-tumor response (20). IL-15 can also be used for the preconditioning of CAR T cells or for engineering cells to express IL-15 in vivo. Adoptive cell transfer of NK cells engineered to express CD19 and IL-15 were well tolerated in patients with CD19-positive cancers (20).
IL-15 can be used in combination with other cytokines like IL-21 to increase the efficiency of NK cell expansion and maturation in stem cell culture protocols (21). The combination of IL-15 with IL-7 also promotes expansion of early-differentiated CD8+ T cells in culture with the added benefit of decreasing Treg cell generation, unlike IL-2, for adoptive cell transfer in cancer immunotherapy (22). GMP IL-7 and GMP IL-15 are commonly used in combination for ex vivo expansion of T cells for cellular therapies.
- De Sabatino, A. et al. (2011) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:19.
- Grabstein, K. et al. (1994) Science 264:965.
- Tagaya, Y. et al. (1997) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:14444.
- Giri, J.G. et al. (1995) EMBO J. 14:3654.
- Giri, J. et al. (1994) EMBO J. 13:2822.
- Dubois, S. et al. (2002) Immunity 17:537.
- Castillo, E.F. and K.S. Schluns (2012) Cytokine 59:479.
- Budagian, V. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:40368.
- Mortier, E. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:1681.
- Bergamaschi, C. et al. (2012) Blood 120:e1.
- Budagian, V. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:42192.
- Mortier, E. et al. (2003) J. Exp. Med. 205:1213.
- Gordy, L.E. et al. (2011) J. Immunol. 187:6335.
- Harris, K.M. (2011) J. Leukoc. Biol. 90:727.
- Xia, J. et al. (2010) Clin. Immunol. 134:130.
- Schluns, K.S. et al. (2002) J. Immunol. 168:4827.
- Davies, E. et al. (2010) J. Leukoc. Biol. 88:529.
- Barra, N.G. et al. (2010) Obesity 18:1601.
- Xue, D. et al. (2021) Antib Ther. 4:123.
- Wolfarth, A.A. et al. (2022) Immune Netw. 22:e5.
- Oberoi, P. et al. (2020). Cells. 9:811.
- Chamucero-Millares, J.A. et al. (2021) Cellular Immunol. 360:104257.