全部商品分类
全部商品分类



 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Scientific Data
 View Larger
View LargerRecombinant Mouse IL-1 beta /IL-1F2 (Catalog # 401-ML) stimulates cell proliferation of the D10.G4.1 mouse helper T cell line. The ED50 for this effect is 2‑10 pg/mL.
 View Larger
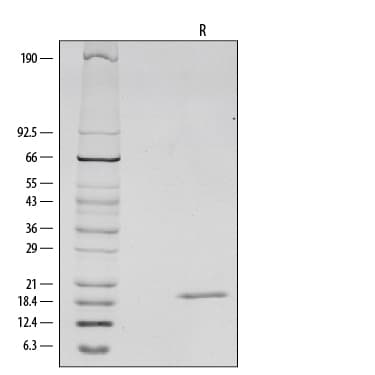
View Larger1 μg/lane of Recombinant Mouse IL1 beta /IL-1F2 was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) conditions and visualized by silver staining, showing a single band at 19 kDa.
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
401-ML
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
401-ML/CF
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Recombinant Mouse IL-1 beta/IL-1F2 Protein Summary
Product Specifications
Val118-Ser269, with an N-terminal Met
Analysis

Background: IL-1 beta/IL-1F2
IL-1 is a name that designates two pleiotropic cytokines, IL-1 alpha (IL-1F1) and IL-1 beta (IL-1F2), which are the products of distinct genes. IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta are structurally related polypeptides that share approximately 17% amino acid (aa) identity in mouse. Both proteins are produced by a wide variety of cells in response to inflammatory agents, infections, or microbial endotoxins. While IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta are regulated independently, they bind to the same receptor and exert identical biological effects. IL-1 RI binds directly to IL-1 alpha or IL-1 beta and then associates with IL-1 R accessory protein (IL-1 R3/IL-1 R AcP) to form a high-affinity receptor complex that is competent for signal transduction. IL-1 RII has high affinity for IL-1 beta but functions as a decoy receptor and negative regulator of IL-1 beta activity. IL-1ra functions as a competitive antagonist by preventing IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta from interacting with IL-1 RI (1-4). The mouse IL-1 beta cDNA encodes a 269 aa precursor. A 117 aa propeptide is cleaved intracellularly by the cysteine protease IL-1 beta -converting enzyme (Caspase-1/ICE) to generate the active cytokine (5, 6). The 17 kDa mature mouse IL-1 beta shares 90% aa sequence identity with cotton rat and rat and 65%-78% identity with canine, equine, feline, human, porcine, and rhesus IL-1 beta.
- Allan, S.M. et al. (2005) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5:629.
- Boraschi, D. and A. Tagliabue (2006) Vitam. Horm. 74:229.
- Kornman, K.S. (2006) Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 83:475S.
- Isoda, K. and F. Ohsuzu (2006) J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 13:21.
- Gray, P.W. et al. (1986) J. Immunol. 137:3644.
- Martinon, F. and J. Tschopp (2007) Cell Death Differ. 14:10.