全部商品分类
全部商品分类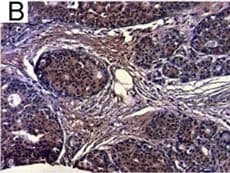


 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
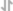 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Immunocytochemistry(5-15 µg/mL)



Pro29-Met212
Accession # P05231

Scientific Data
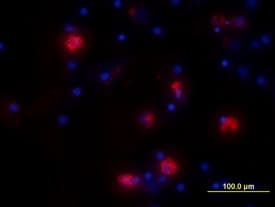
 View Larger
View LargerIL‑6 in Human PBMCs. IL-6 was detected in immersion fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) treated with LPS and monensin using Goat Anti-Human IL-6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF-206-NA) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counter-stained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
 View Larger
View LargerCell Proliferation Induced by IL‑6 and Neutralization by Human IL‑6 Antibody. Recombinant Human IL-6 (Catalog # 206-IL) stimulates proliferation in the T1165.85.2.1 mouse plasmacytoma cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Human IL-6 (2.5 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Human IL-6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF-206-NA). The ND50 is typically ≤ 125 ng/mL.
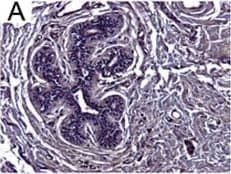
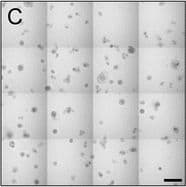
 View Larger
View LargerDetection of Human IL-6 by Immunohistochemistry Breast DCIS cells overexpress proinflammatory markers. Representative images of immunohistochemistry targeting IL-6 protein in normal breast tissue (a), and breast DCIS (b) (N = 61). c and d Hematoxylin staining of serial sections from tissue shown in panel A and B. All images are 20X magnification. Scale bar equals 100 μm. e Evaluation of IL-6 gene expression in DCIS cells via qRT-PCR; the isogenic MCF10.DCIS cells and the non-isogenic SUM102 cell line were analyzed against the non-transformed MCF10A cell line (N = 3). f Secretion of IL-6 protein from DCIS cell lines and non-transformed MCF10A cells as determined by ELISA. *P < 0.05, Student’s t-test; mean ± SD Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26268945), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
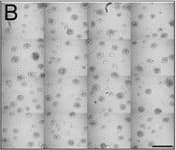
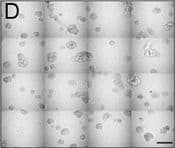
 View Larger
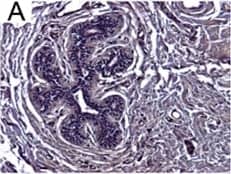
View LargerDetection of Human IL-6 by Block/Neutralize IL-6 neutralizing antibody (nAb) inhibits growth of MCF10.DCIS structures. Representative contiguous 16-tiled DIC images of MCF10.DCIS cells grown in MAME cultures for 8 days. MAME culture of MCF10.DCIS cells treated with an isotype-matched antibody against IgG (control) (8 days) (a), or 1 μg /ml IL-6 nAb (b) (8 days). MCF10.DCIS cells treated with IL-6 nAb followed by a 48 h treatment-free recovery period prior to imaging on day 10 (c). N = 3, Scale bars, 200 μm. d Diameter of MCF10.DCIS structures in the presence of control antibody, IL-6 nAb, or 48 h recovery from IL-6 nAb. N = 20-40 measurements /tiled DIC image (N = 3). ****P ≤ 0.0001, **P ≤ 0.01. e Evaluation of gene expression of invasive tumor cell markers in MAME cultures treated with IL-6 nAb (N = 3). Fold difference as compared to control cultures. Dashed line indicates 2-fold threshold. Student’s t-test; mean ± SD Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26268945), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
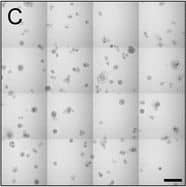
View LargerDetection of Human IL-6 by Block/Neutralize IL-6 nAb inhibits CAF-stimulated MCF10.DCIS structure growth and results in altered morphology. Contiguous 16-tile DIC image of CAFs: WS12Ti (A, B) or CAF40TKi (c, d) co-cultured with MCF10.DCIS cells for 8 days in the presence of isotype matched anti-IgG (a, c) or 1 μg /ml IL-6 nAb (b, d). e Perimeter measurements from DCIS structures in MAME culture in the presence of anti-IgG or IL-6 nAb (N = 100-140 measurements from 6 contiguous tiled DIC images (N = 3). Fluorescent tiled images of CAF40TKi fibroblasts (unlabeled) cultured with MCF10.DCIS-RFP cells in the presence of anti-IgG (f) or 1 μg /ml IL-6 nAb (g). h Quantification of total volume of DCIS-RFP structures in co-culture with CAF40TKi fibroblasts (ratio-paired t-test, N = 3). ***P ≤ 0.001, **P ≤ 0.01; Student’s t-test; mean ± SD Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26268945), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
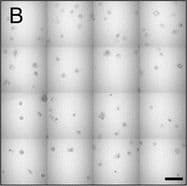
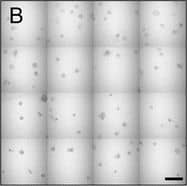 View Larger
View LargerDetection of Human IL-6 by Block/Neutralize IL-6 neutralizing antibody (nAb) inhibits growth of MCF10.DCIS structures. Representative contiguous 16-tiled DIC images of MCF10.DCIS cells grown in MAME cultures for 8 days. MAME culture of MCF10.DCIS cells treated with an isotype-matched antibody against IgG (control) (8 days) (a), or 1 μg /ml IL-6 nAb (b) (8 days). MCF10.DCIS cells treated with IL-6 nAb followed by a 48 h treatment-free recovery period prior to imaging on day 10 (c). N = 3, Scale bars, 200 μm. d Diameter of MCF10.DCIS structures in the presence of control antibody, IL-6 nAb, or 48 h recovery from IL-6 nAb. N = 20-40 measurements /tiled DIC image (N = 3). ****P ≤ 0.0001, **P ≤ 0.01. e Evaluation of gene expression of invasive tumor cell markers in MAME cultures treated with IL-6 nAb (N = 3). Fold difference as compared to control cultures. Dashed line indicates 2-fold threshold. Student’s t-test; mean ± SD Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26268945), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
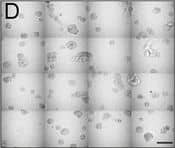 View Larger
View LargerDetection of Human IL-6 by Block/Neutralize IL-6 nAb inhibits CAF-stimulated MCF10.DCIS structure growth and results in altered morphology. Contiguous 16-tile DIC image of CAFs: WS12Ti (A, B) or CAF40TKi (c, d) co-cultured with MCF10.DCIS cells for 8 days in the presence of isotype matched anti-IgG (a, c) or 1 μg /ml IL-6 nAb (b, d). e Perimeter measurements from DCIS structures in MAME culture in the presence of anti-IgG or IL-6 nAb (N = 100-140 measurements from 6 contiguous tiled DIC images (N = 3). Fluorescent tiled images of CAF40TKi fibroblasts (unlabeled) cultured with MCF10.DCIS-RFP cells in the presence of anti-IgG (f) or 1 μg /ml IL-6 nAb (g). h Quantification of total volume of DCIS-RFP structures in co-culture with CAF40TKi fibroblasts (ratio-paired t-test, N = 3). ***P ≤ 0.001, **P ≤ 0.01; Student’s t-test; mean ± SD Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26268945), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
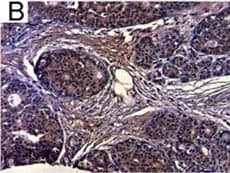 View Larger
View LargerDetection of Human IL-6 by Immunohistochemistry Breast DCIS cells overexpress proinflammatory markers. Representative images of immunohistochemistry targeting IL-6 protein in normal breast tissue (a), and breast DCIS (b) (N = 61). c and d Hematoxylin staining of serial sections from tissue shown in panel A and B. All images are 20X magnification. Scale bar equals 100 μm. e Evaluation of IL-6 gene expression in DCIS cells via qRT-PCR; the isogenic MCF10.DCIS cells and the non-isogenic SUM102 cell line were analyzed against the non-transformed MCF10A cell line (N = 3). f Secretion of IL-6 protein from DCIS cell lines and non-transformed MCF10A cells as determined by ELISA. *P < 0.05, Student’s t-test; mean ± SD Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26268945), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Human IL-6 Antibody Summary
Pro29-Met212
Accession # P05231
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.

Background: IL-6
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pleiotropic, alpha -helical, phosphorylated and variably glycosylated cytokine that plays important roles in the acute phase reaction, inflammation, hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and cancer progression. Mature human IL-6 is 183 amino acids (aa) in length expressed as a 22-28 kDA molecular weight protein. IL-6 shares 39% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat IL-6. Alternative splicing generates several isoforms with internal deletions, some of which exhibit antagonistic properties. IL-6 induces signaling through a cell surface heterodimeric receptor complex composed of a ligand binding subunit (IL-6 R alpha) and a signal transducing subunit (gp130). IL-6 binds to IL-6 R alpha, triggering IL-6 R alpha association with gp130 and gp130 dimerization. gp130 is also a component of the receptors for CLC, CNTF, CT-1, IL-11, IL-27, LIF, and OSM. Soluble forms of IL-6 R alpha are generated by both alternative splicing and proteolytic cleavage. In a mechanism known as trans-signaling, complexes of soluble IL-6 and IL-6 R alpha elicit responses from gp130-expressing cells that lack cell surface IL-6 R alpha. Trans-signaling enables a wider range of cell types to respond to IL-6, as the expression of gp130 is ubiquitous, while that of IL-6 R alpha is predominantly restricted to hepatocytes, monocytes, and resting lymphocytes. Soluble splice forms of gp130 block trans-signaling from IL-6/IL-6 R alpha but not from other cytokines that use gp130 as a co-receptor. IL-6, along with TNF-alpha and IL-1, function to drive the acute inflammatory response and the transition from acute inflammation to either acquired immunity or chronic inflammatory disease. When dysregulated, it contributes to chronic inflammation in obesity, insulin resistance, inflammatory bowel disease, arthritis, sepsis, and atherosclerosis. IL-6 can also function as an anti-inflammatory molecule, as in skeletal muscle where it is secreted in response to exercise. In addition, it enhances hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and the differentiation of Th17 cells, memory B cells, and plasma cells.


Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
参考图片
Detection of Human IL‑6 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) untreated (-) or treated (+) with PHA. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.2 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human IL‑6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF-206-NA) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for IL‑6 at approximately 20-22 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
IL‑6 in Human PBMCs. IL‑6 was detected in immersion fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) treated with LPS and monensin using Goat Anti-Human IL‑6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF-206-NA) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.
Cell Proliferation Induced by IL‑6 and Neutralization by Human IL‑6 Antibody. Recombinant Human IL‑6 (Catalog # 206-IL) stimulates proliferation in the T1165.85.2.1 mouse plasmacytoma cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Human IL‑6 (2.5 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Human IL‑6 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF-206-NA). The ND50 is typically 15-45 ng/mL.