 全部商品分类
全部商品分类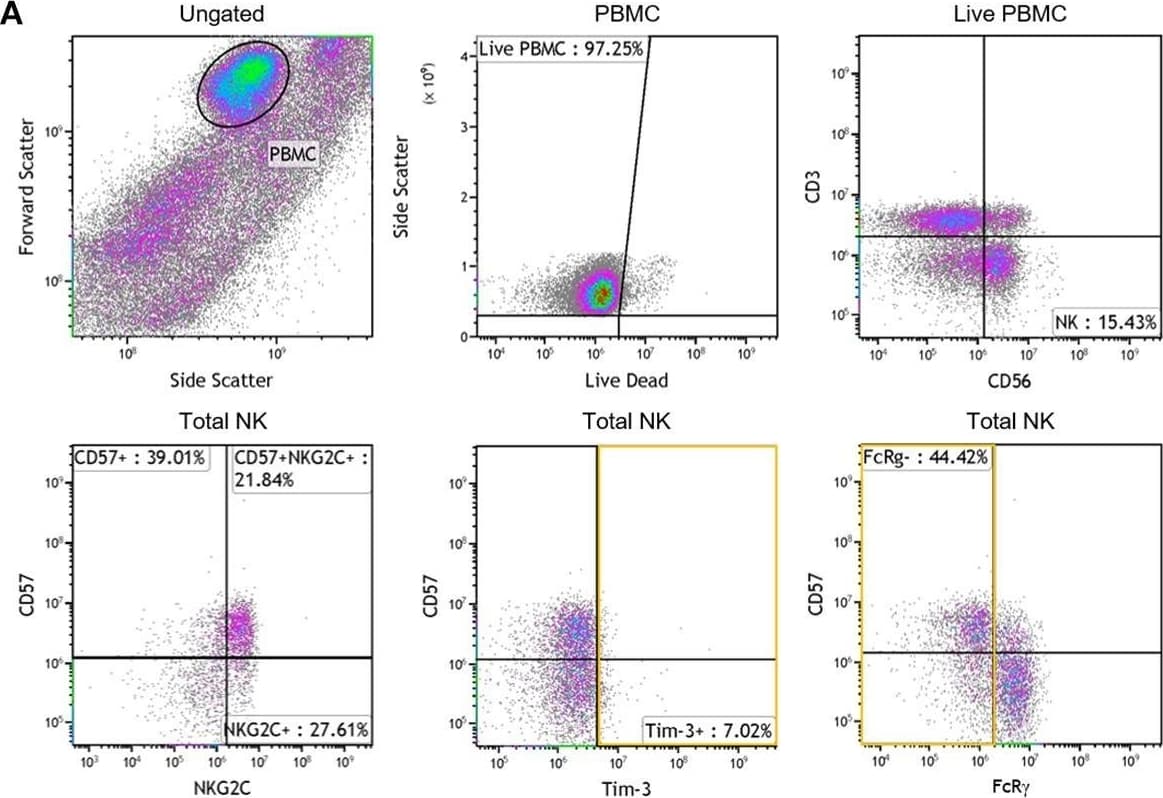

 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询




Scientific Data
 View Larger
View LargerDetection of Human NKG2C/CD159c/KLRC2 by Flow Cytometry Phenotypic characterization of NK cells from HIV-infected individuals with different levels of adaptation to HCMV infection. To identify the NK cell population, (A) PBMC were selected and dead cells excluded. NK cells were identified by expression of CD56 in the absence of CD3 and further characterized for percentage expressing NKG2C, CD57, Tim-3, and FcR gamma in a representative plot. Summary plots depict the percentage of total NK cells that are positive for (B) NKG2C or (C) FcR gamma. Individual donors were grouped based on HCMV serostatus (HCMVneg) and fraction of NK cells expressing NKG2C within the HCMVpos donors (NKG2Clo or NKG2Chi). Correlation between NK cell NKG2C and FcR gamma expression was assessed in (D) with Spearman correlation coefficient (r) calculated and the probability of a significant correlation (p) shown on the graph. Error bars in (B) for the HCMVneg group represent median with IQR, while all others represent mean ± SD. Groups were compared using Mann–Whitney U-tests. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30483249), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Human NKG2C/CD159c Antibody Summary
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.


Background: NKG2C/CD159c
Human NKG2C (NK cell Group 2 isoform C; Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily C, member 2) is a member of the C-type lectin-like superfamily of proteins. Natural killer (NK) receptors are expressed in both NK cells and cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and have both activating and inhibitory members (1-3). Regulation of the balance between the activating and inhibitory receptors is important and lack of such regulation has been implicated in autoimmunity (4). The NKG2 family includes seven receptors: NKG2A, -B, -C, -D, -E, -F, and -H, which is the longer isoform of NKG2E. Except for NKG2D and NKG2F, the NKG2 family members form heterodimers with CD94 (5, 6). NKG2C interacts with the adapter molecule DAP12 and acts as activating receptor when heterodimerized with CD94 (7). Human NKG2C is synthesized as a 231 amino acid (aa) protein that includes a 70 aa cytoplasmic domain, a 23 aa transmembrane segment, and a 138 aa extracellular domain (ECD). Within the ECD, human NKG2C shares 40% sequence identity with mouse NKG2C. NKG2C-CD94 heterodimers bind to the widely expressed nonclassical MHC-I molecule, HLA-E (Qa-1b in mouse), which presents a peptide derived from the signal peptide of classical MHC-I molecules (8, 9). Triggering the NKG2C-CD94 complex may activate the cytolytic activity and cytokine production of NK and CD8+ T cells (8, 10). Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection promotes the differentiation and expansion of NKG2C+ NK cell subsets, possibly involving a cognate interaction of CD94/NKG2C with ligand(s) displayed by HCMV‑infected cells (11, 12).
- Orbelyan, G.A. et al. (2014) J. Immunol. 193:610.
- Tassi I. et al. (2006) Immnunol Rev. 214:92.
- Lanier, L.L. (2008) Nat. Immunol. 9:495.
- Schleinitz, N. et al. (2010) Immunology. 174:2878.
- Lopez-Botet, M. et al. (2000) Hum. Immunol. 61:7.
- Braud, V.M. et al. (1998) Nature. 391:795.
- Lanier, L.L. (1998) Immunity 8:693.
- Vance, R.E. et al. (1999) J Exp Med 190:1801.
- Kaiser B.K. et al. (2005) J Immunol 174:2878.
- Bellón T. et al. (1999) J Immunol 162:3996.
- Pupuleku A. et al. (2017) Front Immunol. 8:1317.
- Hammer Q. et al. (2018) Nat Immunol. 19:453.


Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.




