首页 抗体 一抗 流式抗体 BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-Cleaved PARP (Asp214)
产品介绍
产品信息
简单描述
PARP (Poly [ADP-Ribose] Polymerase) is a 113-kDa nuclear chromatin-associated enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of ADP-ribose units from NAD
+
to a variety of nuclear proteins including topoisomerases, histones, and PARP itself. The catalytic activity of PARP is increased in cells following DNA damage, and PARP is thought to play an important role in mediating the normal cellular response to DNA damage. Additionally, PARP is a target of the caspase protease activity associated with apoptosis. The PARP protein consists of an N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD) and a C-terminal catalytic domain separated by a central automodification domain. During apoptosis, Caspase-3 cleaves PARP at a recognition site (Asp Glu Val Asp Gly) in the DBD to form 24- and 89-kDa fragments. This process separates the DBD (which is mostly in the 24-kDa fragment) from the catalytic domain (in the 89-kDa fragment) of the enzyme, resulting in the loss of normal PARP function. It has been proposed that inactivation of PARP directs DNA-damaged cells to undergo apoptosis rather than necrotic degradation, and the presence of the 89-kDa PARP cleavage fraction is considered to be a marker of apoptosis.
A peptide corresponding to the N-terminus of the cleavage site (Asp 214) of human PARP was used as the immunogen. The F21-852 monoclonal antibody reacts only with the 89-kDa fragment of human PARP-1 that is downstream of the Caspase-3 cleavage site (Asp214) and contains the automodification and catalytic domains. It does not react with intact human PARP-1. Cross-reactivity with other members of the PARP superfamily is unknown. Recognition of cleaved PARP in mouse cells has been demonstrated, and it may also cross-react with a number of other species due to the conserved nature of the molecule.

应用
实验应用
Western blot (Routinely Tested), Immunoprecipitation, Intracellular staining (flow cytometry) (Tested During Development)
文献
文献
研发参考(6)
1. D'Amours D, Desnoyers S, D'Silva I, Poirier GG. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reactions in the regulation of nucelar functions. Biochem J. 1999; 342:249-268. (Biology).
2. Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Ottaviano Y, Davidson NE, Poirier GG. Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: an early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1993; 53(17):3976-3985. (Biology).
3. Lamarre D, Talbot B, Leduc Y, Muller S, Poirier G. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for the functional domains of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986; 64(4):368-376. (Biology).
4. Lamarre D, Talbot B, de Murcia G, et al. Structural and functional analysis of poly(ADP ribose) polymerase: an immunological study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988; 950(2):147-160. (Biology).
5. Patel T, Gores GJ, Kaufmann SH. The role of proteases during apoptosis. FASEB J. 1996; 10(5):587-597. (Biology).
6. Tewari M, Quan LT, O'Rourke K, et al. Yama/CPP32 beta, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell. 1995; 81(5):801-809. (Biology).

参考图片
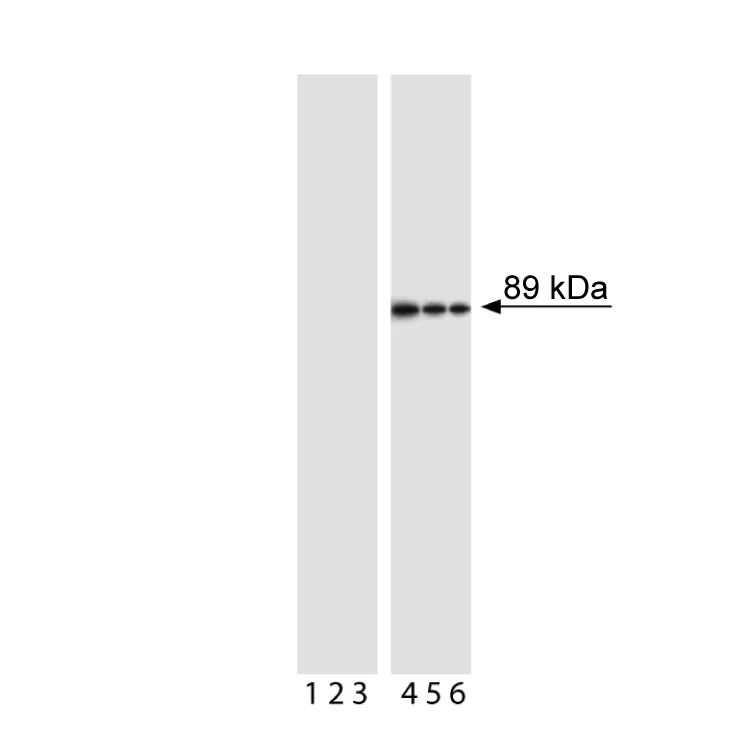
Western blot analysis of PARP (cleavage site-specific). Jurkat cells were either left untreated (lanes 1-3) or treated with camptothecin (4 µM, 4 hours) to induce apoptosis (lanes 4-6). Lysates were probed with anti-PARP (clone F21-852, Cat. No. 552597) at concentrations of 0.25 (lanes 1, 4), 0.125 (lanes 2, 5), and 0.06 µg/ml (lanes 3, 6). Cleaved PARP is identified as a band of ~89 kDa in only the treated cells.
Western blot analysis of PARP (cleavage site-specific). Jurkat cells were either left untreated (lanes 1-3) or treated with camptothecin (4 µM, 4 hours) to induce apoptosis (lanes 4-6). Lysates were probed with anti-PARP (clone F21-852, Cat. No. 552597) at concentrations of 0.25 (lanes 1, 4), 0.125 (lanes 2, 5), and 0.06 µg/ml (lanes 3, 6). Cleaved PARP is identified as a band of ~89 kDa in only the treated cells.
当前规格1件起购
预计3-5周送达,快递: 免运费,若需干冰额外收费
 全部商品分类
全部商品分类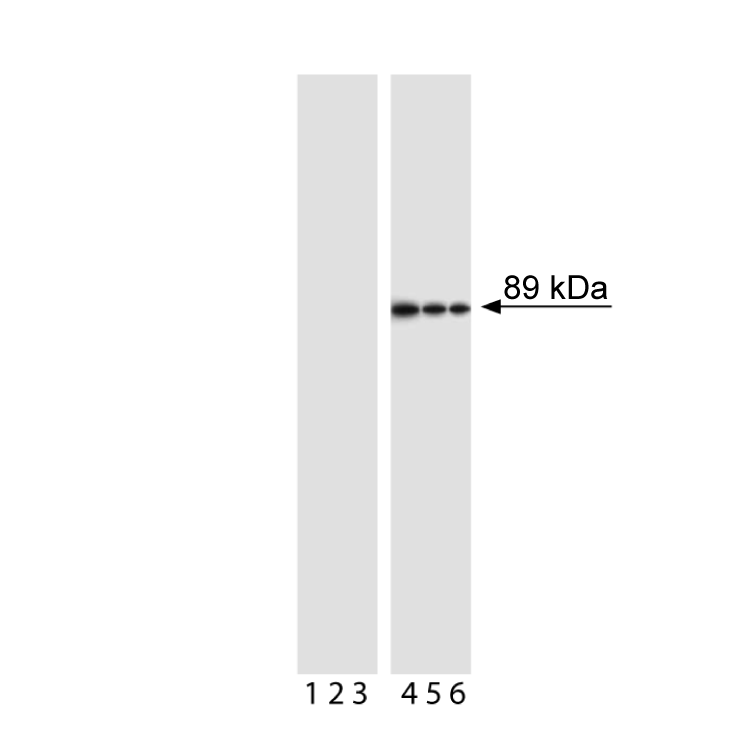

















 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷




