 全部商品分类
全部商品分类

















参考图片
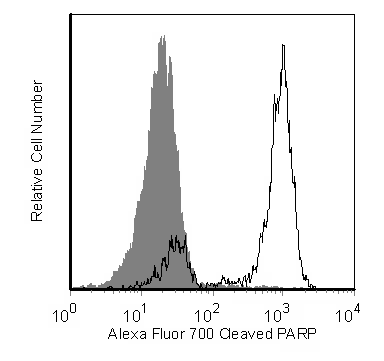
Flow cytometric analysis of cleaved PARP in camptothecin treated Jurkat cells. Jurkat cells (Human T-cell leukemia; ATCC TIB-152) were either untreated (shaded) or treated with 4-6 µM camptothecin (Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. C-9911) (unshaded), fixed and permeabilized with BD Cytofix/Cytoperm™ (Cat. No. 554714) and subsequently stained with the Alexa Fluor® 700 Mouse Anti-Cleaved PARP antibody. Histograms were derived from gated events based on light scattering characteristics for Jurkat cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD™ LSR II flow cytometry system.
Flow cytometric analysis of cleaved PARP in camptothecin treated Jurkat cells. Jurkat cells (Human T-cell leukemia; ATCC TIB-152) were either untreated (shaded) or treated with 4-6 µM camptothecin (Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. C-9911) (unshaded), fixed and permeabilized with BD Cytofix/Cytoperm™ (Cat. No. 554714) and subsequently stained with the Alexa Fluor® 700 Mouse Anti-Cleaved PARP antibody. Histograms were derived from gated events based on light scattering characteristics for Jurkat cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD™ LSR II flow cytometry system.




 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷




