 全部商品分类
全部商品分类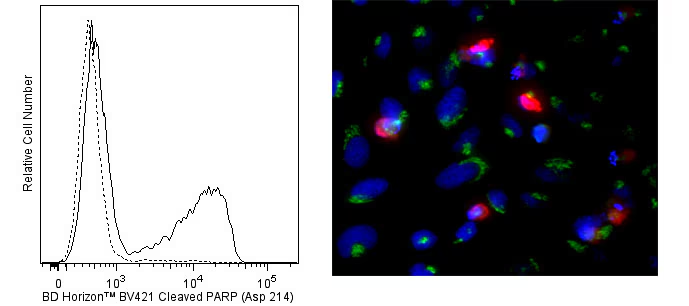



 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询















参考图片
Flow cytometric analysis of cleaved PARP (Asp 214) expression (left panel). Cells from the human Jurkat (ATCC TIB-152) cell line were cultured for 6 hours with (solid line histogram) or without (dashed line histogram) Camptothecin (Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. C-9911; 12 μM final concentration). The cells were harvested, washed with BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) (Cat. No. 554656), and fixed and permeabilized with BD Cytofix/Cytoperm™ Fixation and Permeabilization Solution (Cat. No. 554722). The cells were then washed and stained in BD Perm/Wash™ Buffer (Cat. No. 554723) with BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-Cleaved PARP (Asp 214) antibody (Cat. No. 564129). Histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact Jurkat cells. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System. Immunofluorescent analysis of cleaved PARP in apoptotic human cells (right panel). HeLa cells (ATCC, CCL-2) were treated with camptothecin (20 µM, 6 hours) to induce apoptosis. Cells were then fixed with BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050), and blocked with 5% goat serum, 1% BSA, and 0.5% Triton™ X-100 diluted in PBS. Cells were stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-Cleaved PARP (Asp 214) antibody (Cat. No. 564129, pseudo-colored red) and Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse Anti-GM130 antibody (Cat. No. 560257, pseudo-colored green). DRAQ5 was used as a nuclear counterstain (Cat. No. 564902/564903, pseudo-colored blue). Images were captured on a standard epifluorescence microscope. Original magnification, 20x.
Flow cytometric analysis of cleaved PARP (Asp 214) expression (left panel). Cells from the human Jurkat (ATCC TIB-152) cell line were cultured for 6 hours with (solid line histogram) or without (dashed line histogram) Camptothecin (Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. C-9911; 12 μM final concentration). The cells were harvested, washed with BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) (Cat. No. 554656), and fixed and permeabilized with BD Cytofix/Cytoperm™ Fixation and Permeabilization Solution (Cat. No. 554722). The cells were then washed and stained in BD Perm/Wash™ Buffer (Cat. No. 554723) with BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-Cleaved PARP (Asp 214) antibody (Cat. No. 564129). Histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact Jurkat cells. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System. Immunofluorescent analysis of cleaved PARP in apoptotic human cells (right panel). HeLa cells (ATCC, CCL-2) were treated with camptothecin (20 µM, 6 hours) to induce apoptosis. Cells were then fixed with BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050), and blocked with 5% goat serum, 1% BSA, and 0.5% Triton™ X-100 diluted in PBS. Cells were stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-Cleaved PARP (Asp 214) antibody (Cat. No. 564129, pseudo-colored red) and Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse Anti-GM130 antibody (Cat. No. 560257, pseudo-colored green). DRAQ5 was used as a nuclear counterstain (Cat. No. 564902/564903, pseudo-colored blue). Images were captured on a standard epifluorescence microscope. Original magnification, 20x.





