 全部商品分类
全部商品分类






ELISA
Sandwich ELISA
CLIA
Lateral Flow
Dot Blot
WB
IP
IHC-P
ICC
IF
ICFCM
FCM
mIHC
IFN-α is a cytokine that has an immunomodulatory function. It plays an important role not only in antiviral activity but also in several physiologic functions, such as activation of dendritic cells and accelerated expression of major histocompatibility complex I and II molecules that may cause increased antigen presentation. In humans, the type I IFN system consists of a family of IFN proteins encoded by at least 13 IFN alpha (IFNA) subtype genes (IFN-α1, -α2, -α4, -α5, -α6, -α7, -α8, -α10, -α13, -α14, -α16, -α17 and -α21), and one IFN beta gene (IFNB), one IFN-Epsilon gene, one IFN-Kappa gene, and IFN-Omega gene, all of which bind to the type I interferon receptor composed of the IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 chains.

12 months from date of receipt / reconstitution, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
参考图片
Standard curve
Example of Human IFN-α standard curve in Assay Diluent #1.
Linearity
The concentrations of IFN-α were measured and interpolated from the target standard curves and corrected for sample dilution.
Sample is undiluted samples are as follows: human PBMC cells stimulated with 10ug/ml PHA for 5days (100%). The interpolated dilution factor corrected values are plotted. The mean target concentration was determined to be 19.41 pg/mL in stimulated human PBMC supernatant.
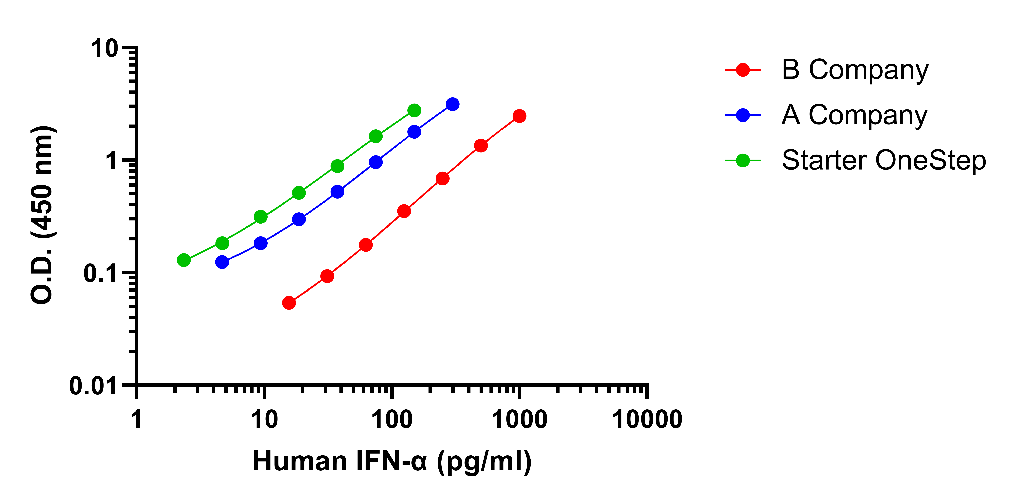
Leading Competitor comparison
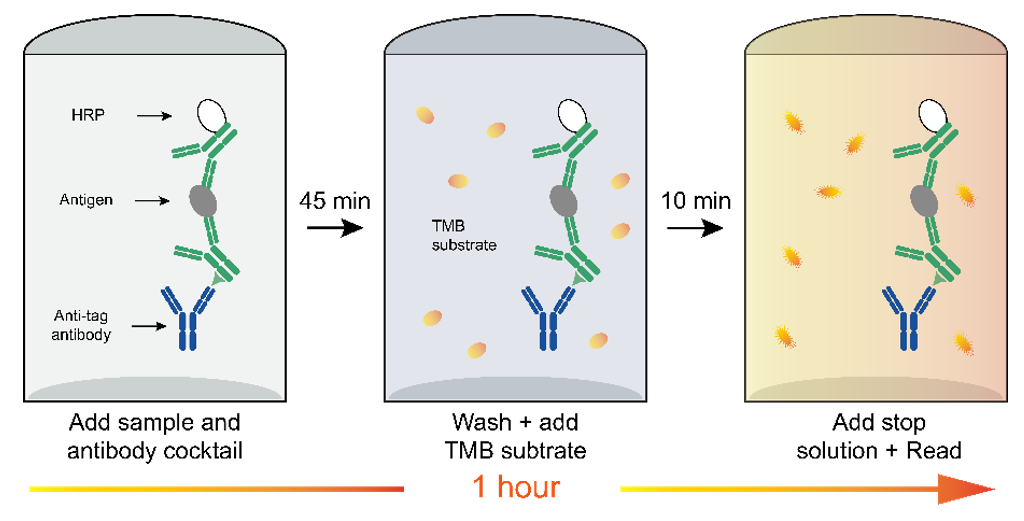
Protocol Diagram




 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷




