Tau is a heterogeneous microtubule-associated protein that promotes and stabilizes microtubule assembly, especially in axons. Six isoforms with different amino-terminal inserts and different numbers of tandem repeats near the carboxy terminus have been identified, and tau is hyperphosphorylated at approximately 25 sites by Erk, glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3), and CDK5 (1,2). Phosphorylation decreases the ability of tau to bind to microtubules. Neurofibrillary tangles are a major hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD); these tangles are bundles of paired helical filaments (PHFs) composed of hyperphosphorylated tau. In particular, phosphorylation at Ser396 by GSK-3 or CDK5 destabilizes microtubules. Furthermore, research studies have shown that inclusions of tau are found in a number of other neurodegenerative diseases, collectively known as tauopathies (1,3).Alternative splicing of exon 10 results in the expression of two groups of tau: three-repeat and four-repeat tau. Isoforms 2, 4, and 5 express three microtubule binding repeat domains (tau 3R) while isoforms 6, 7, and 8 express four microtubule binding repeat domains (tau 4R) (4). Expression of tau 3R and tau 4R in cells can be different in mild or pathological conditions. For example, tau 3R is preferentially expressed in Pick's disease (PiD) and corticobasal degeneration (CBD), while tau 3R and tau 4R are equally expressed in AD (5,6). The repeat-dependent tau has a different pattern of phosphorylation in different diseases and also has the ability and patterns of aggregation (7-9).
1.Johnson, G.V. and Stoothoff, W.H. (2004) J Cell Sci 117, 5721-9.
2.Hanger, D.P. et al. (1998) J Neurochem 71, 2465-76.
3.Bramblett, G.T. et al. (1993) Neuron 10, 1089-99.
4.Šimić, G. et al. (2016) Biomolecules 6, 6.
5.Tuerde, D. et al. (2018) J Biol Chem 293, 1781-1793.
6.Liu, C. and Götz, J. (2013) PLoS One 8, e84849.
7.Weismiller, H.A. et al. (2018) J Biol Chem 293, 17336-17348.
8.Goedert, M. et al. (2018) Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 83, 163-171.
9.Kraus, A. et al. (2019) Acta Neuropathol 137, 585-598.
 全部商品分类
全部商品分类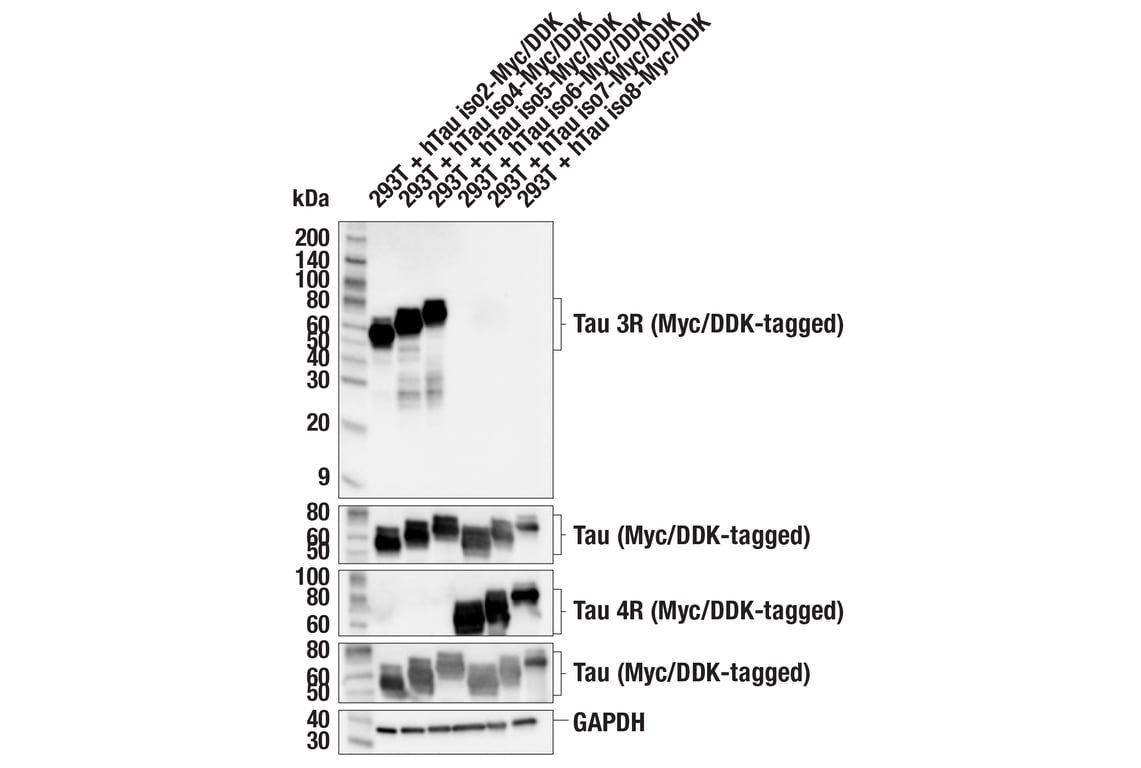


















 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷




