全部商品分类
全部商品分类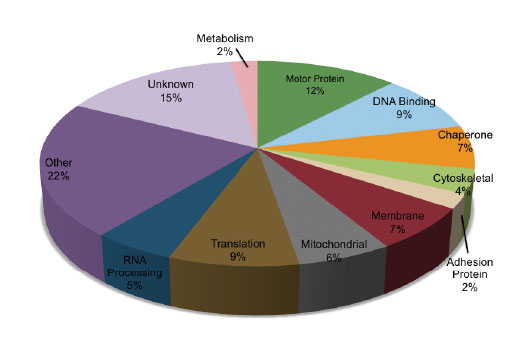



 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询PTMScan® Technology employs a proprietary methodology from Cell Signaling Technology (CST) for peptide enrichment by immunoprecipitation using a specific bead-conjugated antibody in conjunction with liquid chromatography (LC) tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) for quantitative profiling of post-translational modification (PTM) sites in cellular proteins. These include phosphorylation (PhosphoScan®), ubiquitination (UbiScan®), acetylation (AcetylScan®), and methylation (MethylScan®), among others. PTMScan® Technology enables researchers to isolate, identify, and quantitate large numbers of post-translationally modified cellular peptides with a high degree of specificity and sensitivity, providing a global overview of PTMs in cell and tissue samples without preconceived biases about where these modified sites occur. For more information on PTMScan® Proteomics Services, please visit www.cellsignal.com/common/content/content.jsp?id=proteomics.

Product Usage Information
Cells are lysed in a urea-containing buffer, cellular proteins are digested by proteases, and the resulting peptides are purified by reversed-phase solid-phase extraction. Peptides are then subjected to immunoaffinity purification using a PTMScan® Motif Antibody conjugated to protein A agarose beads. Unbound peptides are removed through washing, and the captured PTM-containing peptides are eluted with dilute acid. Reversed-phase purification is performed on microtips to desalt and separate peptides from antibody prior to concentrating the enriched peptides for LC-MS/MS analysis. CST recommends the use of PTMScan® IAP Buffer #9993 included in the kit. PTMScan® Pan-Methyl Lysine Kit Kit has a higher sensitivity and specificity magnetic bead version: PTMScan® HS Pan-Methyl Lysine Kit in 10-assay (#28411) or 3-assay (#25012) formats.



Antibody beads supplied in IAP buffer containing 50% glycerol. Store at -20°C. Do not aliquot the antibody.
参考图片
The chart shows the relative category distribution of proteins with methylated lysine residues derived from peptides identified from a MethylScan® LC-MS/MS experiment of mouse liver tissue using PTMScan® Pan-Methyl Lysine Immunoaffinity Beads. Within this set of 130 peptides, the frequency of mono-methylated lysine peptides is 64%, di-methylated lysine peptide frequency is 24%, and tri-methyl lysine peptides comprise 12% of the sample.
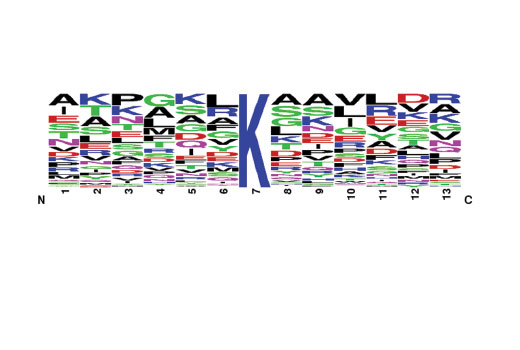
The Motif Logo was generated from a MethylScan® LC-MS/MS experiment using 130 nonredundant tryptic peptides derived from mouse liver tissue immunoprecipitated with PTMScan® Pan-Methyl Lysine Immunoaffinity Beads. The logo represents the relative frequency of amino acids in each position surrounding the central methylated lysine residue within this data set.