 全部商品分类
全部商品分类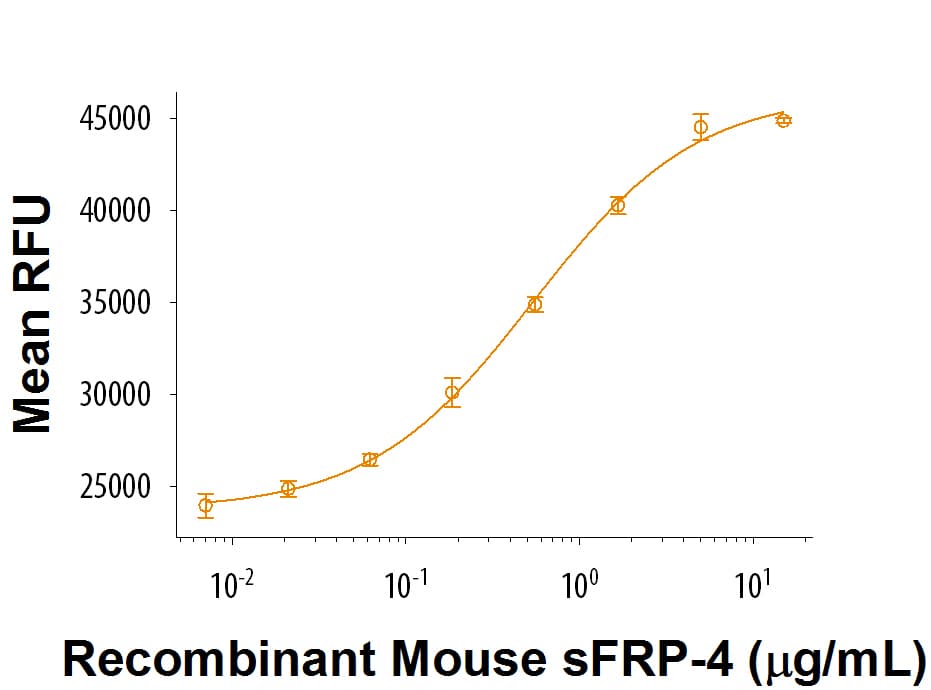

 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Scientific Data
 View Larger
View LargerRecombinant Mouse sFRP-4 (Catalog # 9806-SF) activates Wnt induced TCF reporter activity in HEK293 human embryonic kidney cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.2-1.2 µg/mL in the presence of 5 ng/mL Recombinant Mouse Wnt-3a (Catalog # 1324-WN).
Carrier Free
CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
9806-SF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage: | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Recombinant Mouse sFRP-4 Protein, CF Summary
Product Specifications
Ala22-Ser351
Analysis

Background: sFRP-4
Secreted Frizzled Related Protein-4 (sFRP-4), also known as DDC-4, FrpAP, frpHE and FrzB-2, belongs to a family of Wnt-binding proteins with homology to the ligand-binding domain of the Frizzled receptors (1, 2). The sFRP proteins are approximately 30-35 kDa in size and contain an N-terminal Frizzled-like domain with 10 conserved cysteines and a Netrin-like C-terminal domain (1-3). Of all the sFRPs, sFRP-4 is most closely related to sFRP-3 (1). Mature mouse sFRP-4 shares 92% and 96% amino acid (aa) sequence identity with human and rat sFRP-4, respectively. sFRP-4 is expressed in brain, kidney, lung, ovary, prostate, mammary gland, and endometrium (1, 2). This protein shows complex functions with respect to cell survival: it is up‑regulated with apoptosis during ovulation (3), regulates apoptosis in chondrocytes (4), and promotes apoptosis in mammary glands when expressed in transgenic mice (5). On the other hand, sFRP-4 can also act to enhance growth as it is up‑regulated in endometrial and breast carcinomas (6, 7). Since it is not detected in other carcinomas such as the ovary, colon, and pancreas, its role in cancer is likely to be tissue dependent (6). In addition, sFRP-4 is characterized as a circulating phosphaturic factor expressed by tumors associated with osteomalacia that antagonizes renal Wnt signaling (8).
- Jones, S.E. and C. Jomary (2002) Bioessays 24:811.
- Wolf, V. et al. (1997) FEBS Letters 417:385.
- Drake, J.M. et al. (2003) Apoptosis 8:389.
- James, I.E. et al. (2000) Osteoarthritis & Cartilage 8:452.
- Lacher, M.D. et al. (2003) Cell Death Differ. 10:528.
- Abu-Jawdeh, G. et al. (1999) Lab Invest. 79:439.
- Wong, S.C. et al. (2002) J. Pathol. 196:145.
- Berndt, T. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Invest. 112:785.





