 全部商品分类
全部商品分类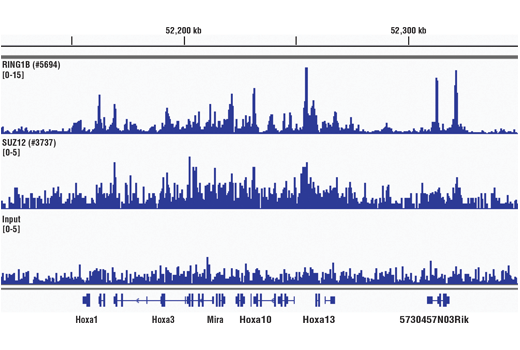


The SimpleChIP® Plus Sonication Chromatin IP Kit is a complete ChIP kit. It contains the buffers and reagents necessary to perform up to 24 chromatin immunoprecipitations from cells or tissue samples, and is optimized for 4 X 106 cells or 25 mg of tissue per immunoprecipitation. A complete assay can be performed in as little as two days and can easily be scaled up or down for use with more or less cells or tissue sample. This kit is compatible with both ChIP-qPCR and ChIP-seq.
Cells or tissue are fixed with formaldehyde and lysed, and chromatin is fragmented by sonication to obtain chromatin fragments ranging from 200 to 1000 bp. Sonication-based fragmentation is the more traditional method for fragmenting chromatin; however, sonication should be optimized such that the desired fragment size is achieved with the minimal amount of sonication required, as over-sonication can result in a decrease in immunoprecipitation, specifically for transcription factors and cofactors. The cell and nuclear lysis buffers for this kit have been optimized to maximize enrichment of histones, transcription factors and cofactors. Chromatin immunoprecipitations are performed using ChIP-validated antibodies and ChIP-Grade Protein G Magnetic Beads. After reversal of protein-DNA cross-links, the DNA is purified using DNA purification spin columns, allowing for easy and efficient recovery of DNA and removal of protein contaminants without the need for phenol/chloroform extractions and ethanol precipitations. The enrichment of particular DNA sequences during immunoprecipitation can be analyzed by a variety of methods, including standard PCR, quantitative real-time PCR, or amplification for ChIP on chip, sequencing or cloning techniques.
The SimpleChIP® Plus Kit also provides important controls to ensure a successful ChIP experiment. The #56383 sonication ChIP kit contains a positive control Histone H3 Antibody, a negative control Normal Rabbit IgG Antibody, and primer sets for PCR detection of the human and mouse ribosomal protein L30 (RPL30) genes. Histone H3 is a core component of chromatin and is bound to most DNA sequences throughout the genome, including the RPL30 locus. Thus, the Histone H3 Antibody provides a universal positive control that should enrich for almost any locus examined.




Specificity/Sensitivity



All components in this kit are stable for at least 12 months past the reference date indicated on the component label when stored at the recommended temperature and left unused.
参考图片
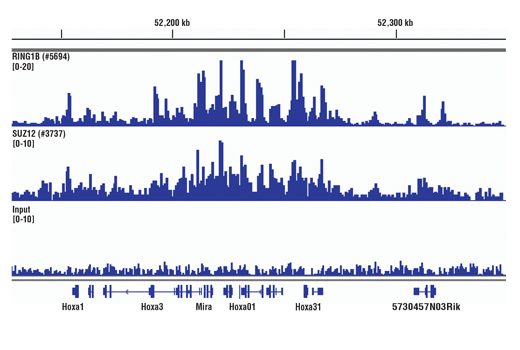
FIGURE 6. Mouse brain was cross-linked for 30 min and disaggregated into a single-cell suspension using a Dounce homogenizer. Chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed with sonicated chromatin and either RING1B (D22F2) XP® Rabbit mAb #5694 or SUZ12 (D39F6) XP® Rabbit mAb #3737 using SimpleChIP® Plus Sonication Chromatin IP Kit #56383. DNA Libraries were prepared using Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN) #56795. RING1B and SUZ12 are components of the PRC1 and PRC2 polycomb repressor complexes respectively, and are known to co-localize on chromatin. The figure shows binding of RING1B and SUZ12 across the HoxA gene cluster, known targets of both RING1B and SUZ12.
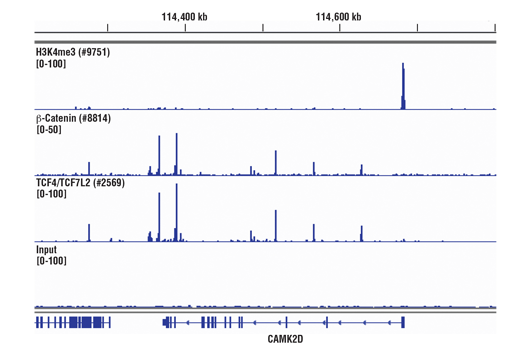
FIGURE 1. Chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed with cross-linked chromatin from HCT 116 cells and either Tri-Methyl-Histone H3 (Lys4) (C42D8) Rabbit mAb #9751, Non-phospho (Active) β-Catenin (Ser33/37/Thr41) (D13A1) Rabbit mAb #8814, or TCF4/TCF7L2 (C48H11) Rabbit mAb #2569 using SimpleChIP® Plus Sonication Chromatin IP Kit #56383. DNA Libraries were prepared using DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN) #56795. The figure shows binding across CAMK2D, a known target gene of H3K4me3, TCF4/TCF7L2, and β-Catenin.
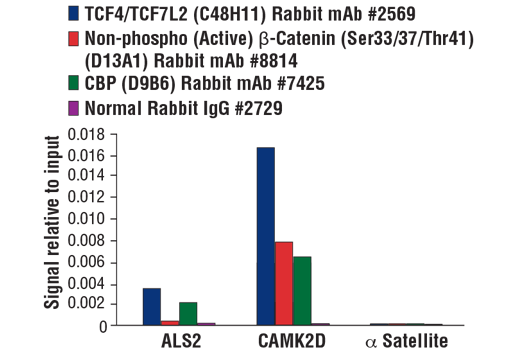
FIGURE 2. Chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed with cross-linked chromatin from HCT 116 cells and either TCF4/TCF7L2 (C48H11) Rabbit mAb #2569, Non-phospho (Active) β-Catenin (Ser33/37/Thr41) (D13A1) Rabbit mAb #8814,CBP (D9B6) Rabbit mAb #7425, or Normal Rabbit IgG #2729 using SimpleChIP® Plus Sonication Chromatin IP Kit #56383. The enriched DNA was quantified by real-time PCR using human ALS2 exon 1 primers, SimpleChIP® Human CaMK2D Intron 3 Primers #5111, and SimpleChIP® Human α Satellite Repeat Primers #4486. The amount of immunoprecipitated DNA in each sample is represented as signal relative to the total amount of input chromatin, which is equivalent to one.
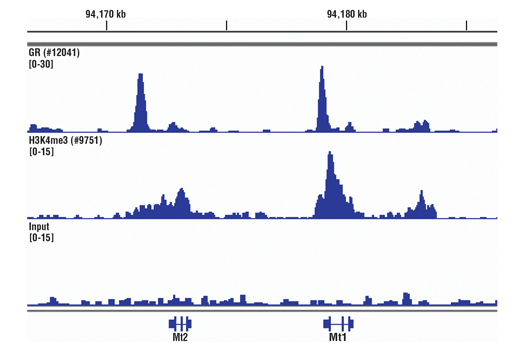
FIGURE 3. Mouse liver was cross-linked for 10 min and disaggregated into a single-cell suspension using a Dounce homogenizer. Chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed with sonicated chromatin and either Glucocorticoid Receptor (D6H2L) XP® Rabbit mAb #12041 or Tri-Methyl-Histone H3 (Lys4) (C42D8) Rabbit mAb #9751 using SimpleChIP® Plus Sonication Chromatin IP Kit #56383. DNA Libraries were prepared using DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN) #56795. The figure shows binding across Mt2, a known target gene of both GR and H3K4me3.
FIGURE 4. Mouse liver was cross-linked for 30 min and disaggregated into a single-cell suspension using a Dounce homogenizer. Chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed with sonicated chromatin and either RING1B (D22F2) XP® Rabbit mAb #5694 or SUZ12 (D39F6) XP® Rabbit mAb #3737 using SimpleChIP® Plus Sonication Chromatin IP Kit #56383. DNA Libraries were prepared using DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN) #56795. RING1B and SUZ12 are components of the PRC1 and PRC2 polycomb repressor complexes respectively, and are known to co-localize on chromatin. The figure shows binding of RING1B and SUZ12 across the HoxA gene cluster, known targets of both RING1B and SUZ12.
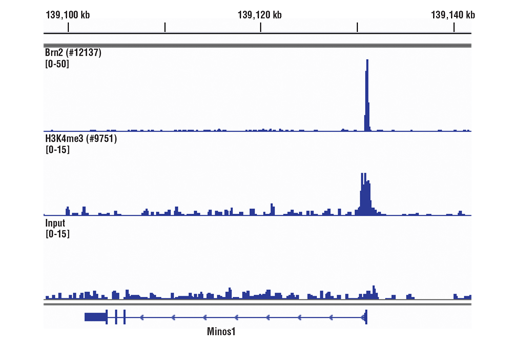
FIGURE 5. Mouse brain was cross-linked for 10 min and disaggregated into a single-cell suspension using a Dounce homogenizer. Chromatin immunoprecipitations were performed with sonicated chromatin and either Brn2/POU3F2 (D2C1L) Rabbit mAb #12137 or Tri-Methyl-Histone H3 (Lys4) (C42D8) Rabbit mAb #9751 using SimpleChIP® Plus Sonication Chromatin IP Kit #56383. DNA Libraries were prepared using DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN) #56795. The figure shows binding across Minos1, a known target gene of both BRN2 and H3K4me3.






 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷




