全部商品分类
全部商品分类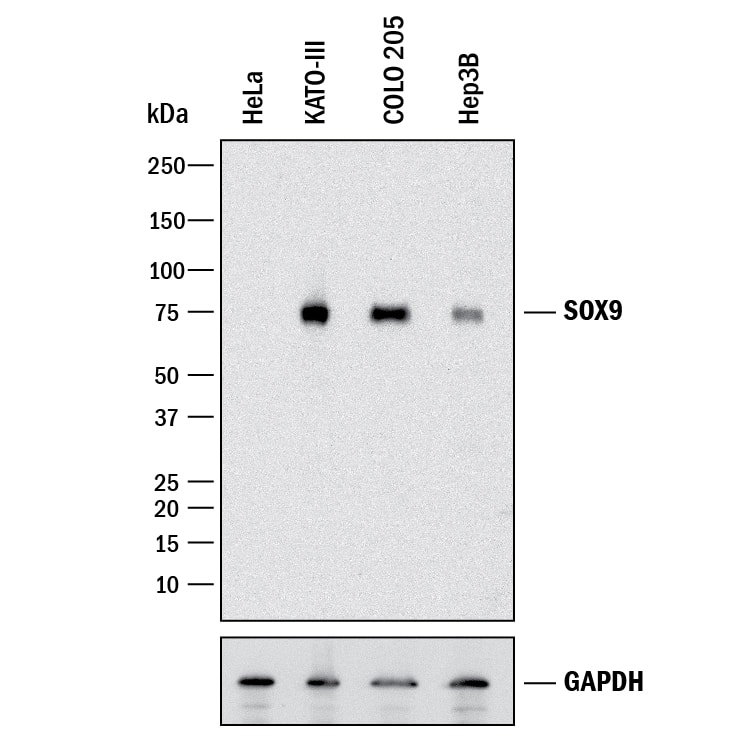



 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询Immunocytochemistry(5-15 µg/mL)



Met1-Lys151
Accession # P48436

Scientific Data
 View Larger
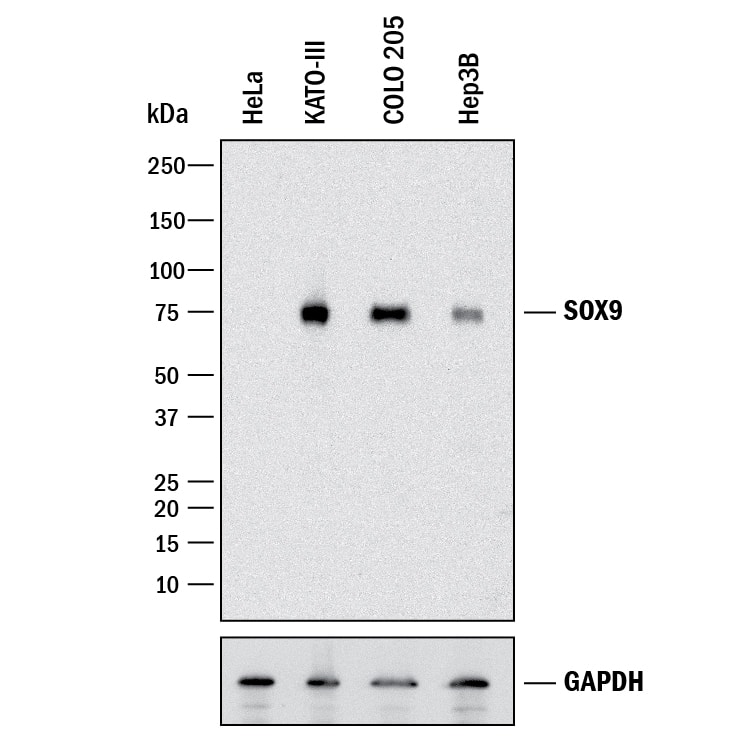
View LargerDetection of Human SOX9 by Western Blot. Western blot shows lysates of HeLa human cervical epithelial carcinoma cell line, KATO-III human gastric carcinoma cell line, COLO 205 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line, and Hep3B human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human SOX9 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3075) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF017). A specific band was detected for SOX9 at approximately 75 kDa (as indicated). GAPDH (Catalog # AF5718) is shown as a loading control. This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.
 View Larger
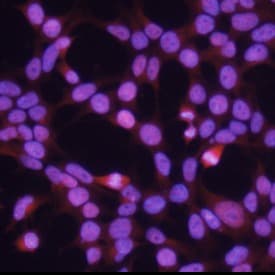
View LargerSOX9 in HEK293 Human Cell Line. SOX9 was detected in immersion fixed HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line using 10 µg/mL Human SOX9 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3075) for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained with the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
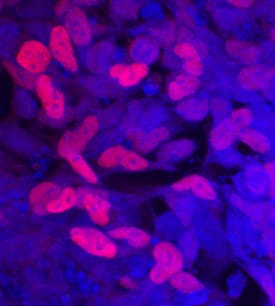
View LargerSOX9 in BG01V Human Embryonic Stem Cells. SOX9 was detected in immersion fixed BG01V human embryonic stem cells differentiated into early proximal lung progenitor cells using Goat Anti-Human SOX9 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3075) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red, upper panel; NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue, lower panel). Specific staining was localized to nuclei. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips.
 View Larger
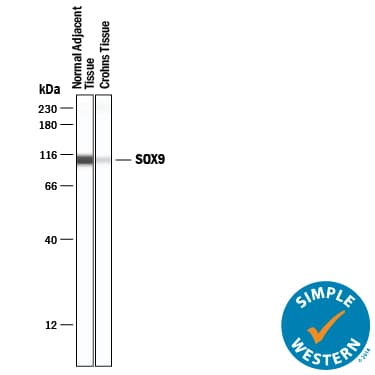
View LargerDetection of Human SOX9 by Simple WesternTM. Simple Western lane view shows lysates of normal adjacent tissue and Crohns tissue, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for SOX9 at approximately 107 kDa (as indicated) using 20 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human SOX9 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3075) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF019). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
 View Larger
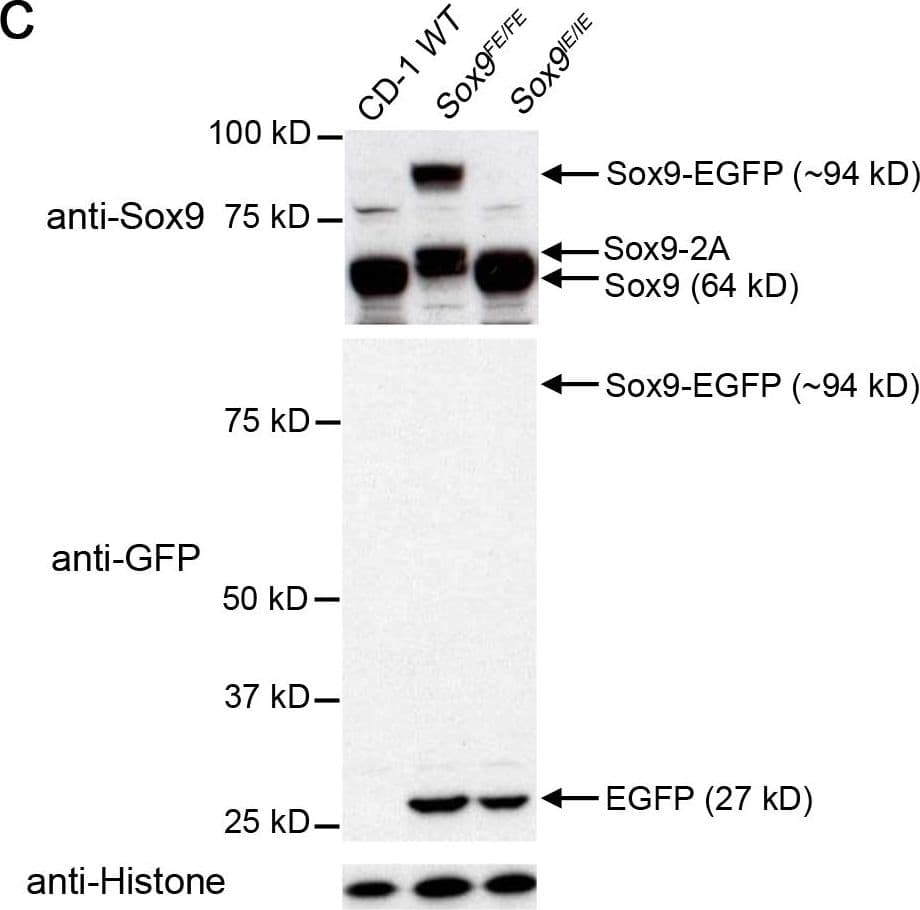
View LargerDetection of Mouse SOX9 by Western Blot Comparison of E12.5 Sox9IE/IE and Sox9FE/FE embryos based on EGFP intensity and Western blotting.(A) Left panel: white light images of E12.5 Sox9IE/IE and Sox9FE/FE embryos; right panel: same embryos imaged by fluorescence microscopy showed a higher EGFP fluorescence in the Sox9FE/FE embryo compared to the Sox9IE/IE embryo, with EGFP expression in Sox9-specific domains in both. (B) Mean overall EGFP fluorescence of E12.5 Sox9IE/IE (13880.04±1015.55; n = 8) and Sox9FE/FE (84579.48±2822.09; n = 4) embryos analyzed by flow cytometry. Overall EGFP fluorescence was calculated by multiplying the MFI and percentage of EGFP-positive cells. Two-tailed Student's T test, ***p<0.0001. (C) Western blot analysis of E12.5 Sox9IE/IE and Sox9FE/FE embryo lysates, resolved on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gels and immunoblotted with anti-Sox9 (upper panel) and anti-GFP (middle panel) antibodies. In the upper panel, Sox9-EGFP fusion protein and Sox9-2A (2A - residual 23 amino acids of F2A) was only detected in the Sox9FE/FE embryo lysate, but not in the CD-1 WT or Sox9IE/IE embryo lysates. Middle panel: Sox9-EGFP fusion protein was not detected in the Sox9FE/FE embryos but EGFP was detected in both the Sox9IE/IE and Sox9FE/FE lysates at predicted molecular weight. CD-1 WT lysate served as negative control for EGFP. Bottom panel: immunoblotting with anti-histone antibody showed equal loading. WT – wild-type. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028885), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
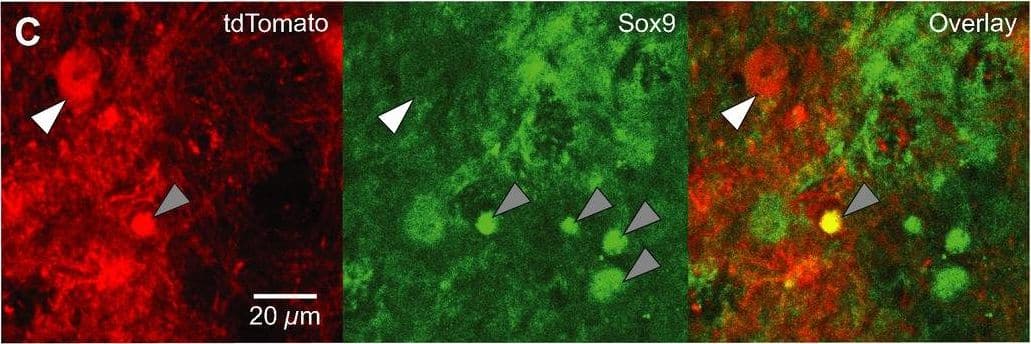
View LargerDetection of Mouse SOX9 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Dbx1‐expressing progenitors give rise to preBötC neurons and glia. A. Confocal images of Dbx1CreERT2; Rosa26tdTomato mouse preBötC sections immunostained for NeuN. Dbx1‐derived neurons (white arrowhead) expressed tdTomato and were immunoreactive for NeuN. Dbx1‐derived glia (gray arrowhead) expressed tdTomato and were not immunoreactive for NeuN. B. Confocal images of Dbx1CreERT2; Rosa26tdTomato mouse preBötC sections 72 h after injection with AAV‐hSyn‐GFP. Dbx1‐derived non‐neuronal cells extend diffuse fibrils that are closely apposed to the outer surface of microvasculature (white arrows). C, Confocal images of Dbx1CreERT2; Rosa26tdTomato mouse preBötC sections immunostained for Sox9. Glia (gray arrowheads) were immunoreactive for Sox9. Dbx1‐derived neurons (white arrowhead) expressed tdTomato but were not immunoreactive for Sox9. Dbx1‐derived glia expressed tdTomato and were immunoreactive for Sox9 (see “overlay” panel). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28611151), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
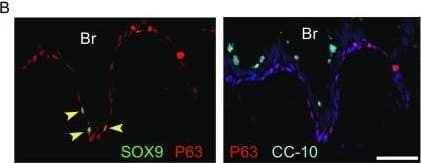
 View Larger
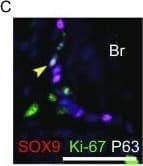
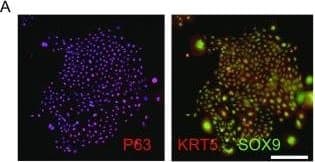
View LargerDetection of Human SOX9 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Feeder-free expansion of SOX9+ BCs. (A) Immunostaining of SOX9+ BCs with anti-P63, anti-KRT5 and anti-SOX9 antibodies. (B) SOX9+ BCs in rugae of 3rd order human airway by anti-SOX9, anti-P63 and anti-CC10 immunostaining. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) SOX9+ BCs in rugae of 3rd order human airway by anti-KI67 immunostaining. (D) BC colony cultured on feeder-free condition. (E) Karyotyping of cultured BCs. (F) qPCR showing alveolar and bronchial epithelium marker gene expression of human lung sample and SOX9+ BCs in early (P2) and late (P8) passages. n = 3, biological replicates. Error bars, S.E.M. (G) qPCR showing progenitor cell marker (Krt5, P63 and SOX9) gene expression of human lung sample and SOX9+ BCs in early (P2) and late (P8) passages. n = 3, biological replicates. Error bars, S.E.M. (H) Western blotting showing marker gene expression of human lung sample and SOX9+ BCs in early (P2) and late (P8) passages Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://academic.oup.com/proteincell/article/9/3/267/6760074), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
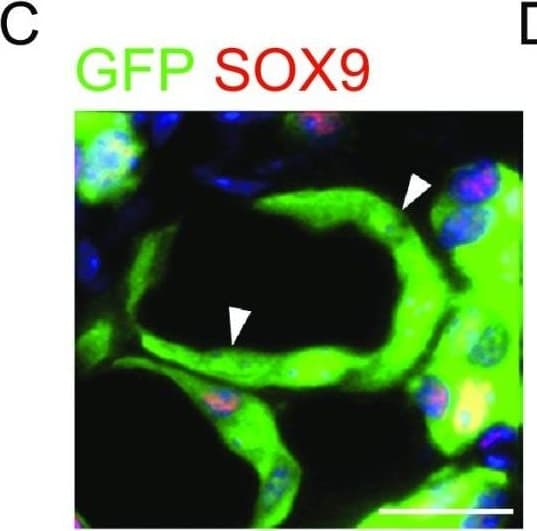
View LargerDetection of Human SOX9 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Transplantated SOX9+ BCs regenerate functional human lungin vivo. (A) Left, direct fluorescence image under stereomicroscope showing NOD-SCID mouse lung without (upper panel) or with (lower panel) GFP-labeled SOX9+ BC transplantation. Right, cryo-section and direct fluorescence imaging of transplanted GFP-labeled SOX9+ BCs in lung parenchyma. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Immunofluorescence imaging of transplanted GFP-labeled SOX9+ BCs in lung parenchyma with human specific Lamin A+C marker costaining. (C) Fully differentiated GFP+ cells lost SOX9 marker expression (arrowhead indicated). Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Confocal image with human specific Lamin A+C immunostaining (HuLamin) showing regenerated type I (AQP5+) alveolar cells. No type II (SPC+) cells were observed. (E) Confocal image showing regenerated AEC1 (AQP5+ and HOPX+). AQP5 as a membrane-bound protein distributes on surface of GFP+ cells. Arrowheads indicated the overlay of HOPX with GFP signal in nucleus. Scale bar, 20 μm. (F) qPCR with human specific primers showing alveolar and bronchiolar epithelium marker gene expression in SOX9+ BC transplanted chimeric lung (AEC1: AQP5 and HOPX; AEC2: SPB and LAMP3; bronchiolar cells: SCGB1A1 and MUC1). Biological replicates, n = 3. Error bars, S.E.M. (G) Left, clonogenic BCs isolated from human cervix epithelium obtained by biopsy. Right, transplantation of equal numbers of BCs from lung and cervix indicated different incorporation efficiency Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://academic.oup.com/proteincell/article/9/3/267/6760074), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View LargerDetection of Human SOX9 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Feeder-free expansion of SOX9+ BCs. (A) Immunostaining of SOX9+ BCs with anti-P63, anti-KRT5 and anti-SOX9 antibodies. (B) SOX9+ BCs in rugae of 3rd order human airway by anti-SOX9, anti-P63 and anti-CC10 immunostaining. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) SOX9+ BCs in rugae of 3rd order human airway by anti-KI67 immunostaining. (D) BC colony cultured on feeder-free condition. (E) Karyotyping of cultured BCs. (F) qPCR showing alveolar and bronchial epithelium marker gene expression of human lung sample and SOX9+ BCs in early (P2) and late (P8) passages. n = 3, biological replicates. Error bars, S.E.M. (G) qPCR showing progenitor cell marker (Krt5, P63 and SOX9) gene expression of human lung sample and SOX9+ BCs in early (P2) and late (P8) passages. n = 3, biological replicates. Error bars, S.E.M. (H) Western blotting showing marker gene expression of human lung sample and SOX9+ BCs in early (P2) and late (P8) passages Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://academic.oup.com/proteincell/article/9/3/267/6760074), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
 View Larger
View LargerDetection of Human SOX9 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence Feeder-free expansion of SOX9+ BCs. (A) Immunostaining of SOX9+ BCs with anti-P63, anti-KRT5 and anti-SOX9 antibodies. (B) SOX9+ BCs in rugae of 3rd order human airway by anti-SOX9, anti-P63 and anti-CC10 immunostaining. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) SOX9+ BCs in rugae of 3rd order human airway by anti-KI67 immunostaining. (D) BC colony cultured on feeder-free condition. (E) Karyotyping of cultured BCs. (F) qPCR showing alveolar and bronchial epithelium marker gene expression of human lung sample and SOX9+ BCs in early (P2) and late (P8) passages. n = 3, biological replicates. Error bars, S.E.M. (G) qPCR showing progenitor cell marker (Krt5, P63 and SOX9) gene expression of human lung sample and SOX9+ BCs in early (P2) and late (P8) passages. n = 3, biological replicates. Error bars, S.E.M. (H) Western blotting showing marker gene expression of human lung sample and SOX9+ BCs in early (P2) and late (P8) passages Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://academic.oup.com/proteincell/article/9/3/267/6760074), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Human SOX9 Antibody Summary
Met1-Lys151
Accession # P48436
Applications
Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website.
Immunocytochemistry(5-15 µg/mL)


Background: SOX9
SOX9 belongs to the SOX (SRY-like HMG box) family of transcription factors with diverse roles in development. SOX9 is expressed in mesenchymal progenitors that give rise to chondrocytes and osteoblasts. It is also expressed in the central nervous system, neural crest, intestine, pancreas, and testis. Mutations in SOX9 are associated with defects in sex determination, cartilage and bone development, as well as abnormalities of the heart, kidneys, brain, gut, and pancreas.


Preparation and Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
参考图片
SOX9 in HEK293 Human Cell Line. SOX9 was detected in immersion fixed HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line using 10 µg/mL Human SOX9 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3075) for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained with the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
SOX9 in BG01V Human Embryonic Stem Cells. SOX9 was detected in immersion fixed BG01V human embryonic stem cells differentiated into early proximal lung progenitor cells using Goat Anti-Human SOX9 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3075) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red, upper panel; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue, lower panel). Specific staining was localized to nuclei. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips.