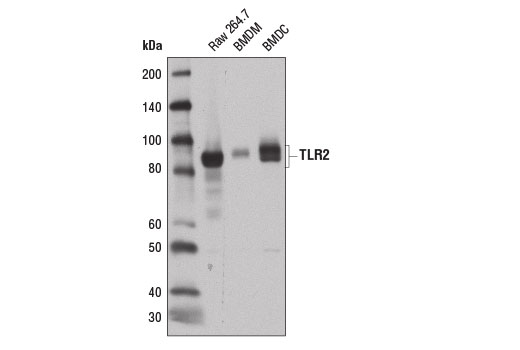
Members of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family, named for the closely related Toll receptor in Drosophila, play a pivotal role in innate immune responses (1-4). TLRs recognize conserved motifs found in various pathogens and mediate defense responses (5-7). Triggering of the TLR pathway leads to the activation of NF-κB and subsequent regulation of immune and inflammatory genes (4). The TLRs and members of the IL-1 receptor family share a conserved stretch of approximately 200 amino acids known as the Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain (1). Upon activation, TLRs associate with a number of cytoplasmic adapter proteins containing TIR domains, including myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), MyD88-adapter-like/TIR-associated protein (MAL/TIRAP), TIR domain-containing adapter-inducing IFN-β (TRIF), and Toll-receptor-associated molecule (TRAM) (8-10). This association leads to the recruitment and activation of IRAK1 and IRAK4, which form a complex with TRAF6 to activate TAK1 and IKK (8,11-14). Activation of IKK leads to the degradation of IκB, which normally maintains NF-κB in an inactive state by sequestering it in the cytoplasm.Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) is expressed on the surface of monocytes and macrophages and can heterodimerize with TLR1 or TLR6, enabling responses to a variety of pathogen-associated molecular signals including lipopeptides and peptidoglycan (15-18).
1.Akira, S. (2003) J Biol Chem 278, 38105-8.
2.Beutler, B. (2004) Nature 430, 257-63.
3.Dunne, A. and O'Neill, L.A. (2003) Sci STKE 2003, re3.
4.Medzhitov, R. et al. (1997) Nature 388, 394-7.
5.Schwandner, R. et al. (1999) J Biol Chem 274, 17406-9.
6.Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11, 443-51.
7.Alexopoulou, L. et al. (2001) Nature 413, 732-8.
8.Zhang, F.X. et al. (1999) J Biol Chem 274, 7611-4.
9.Horng, T. et al. (2001) Nat Immunol 2, 835-41.
10.Oshiumi, H. et al. (2003) Nat Immunol 4, 161-7.
11.Muzio, M. et al. (1997) Science 278, 1612-5.
12.Wesche, H. et al. (1997) Immunity 7, 837-47.
13.Suzuki, N. et al. (2002) Nature 416, 750-6.
14.Irie, T. et al. (2000) FEBS Lett 467, 160-4.
15.Takeuchi, O. et al. (2002) J Immunol 169, 10-4.
16.Schwandner, R. et al. (1999) J Biol Chem 274, 17406-9.
17.Lien, E. et al. (1999) J Biol Chem 274, 33419-25.
18.Ozinsky, A. et al. (2000) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97, 13766-71.
 全部商品分类
全部商品分类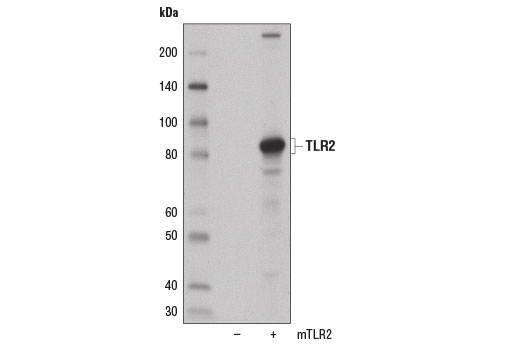


















 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷




