全部商品分类
全部商品分类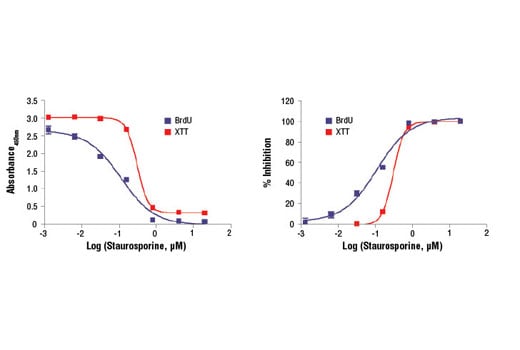



 下载产品说明书
下载产品说明书 下载SDS
下载SDS 用小程序,查商品更便捷
用小程序,查商品更便捷


 收藏
收藏
 对比
对比 咨询
咨询The XTT Cell Viability Assay Kit is a colorimetric assay that detects the cellular metabolic activities. During the assay, the yellow tetrazolium salt XTT is reduced to a highly colored formazan dye by dehydrogenase enzymes in metabolically active cells. This conversion only occurs in viable cells and thus, the amount of the formazan produced is proportional to viable cells in the sample. The formazan dye formed in the assay is soluble in aqueous solution and can be quantified by measuring the absorbance at wavelength 450 nm using a spectrophotometer. An electron coupling reagent, such as PMS (N-Methylphenazonium methyl sulfate), can significantly improve the efficiency of XTT reduction in cells.

Specificity/Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
All Species Expected



参考图片
Figure 3. HeLa cells were seeded at 1x104 cells/well in a 96-well plate and incubated overnight. Cells were then treated with various concentrations of staurosporine overnight. The cytotoxicity was measured using XTT Cell Viability Kit (red) and BrdU Cell Proliferation Assay Kit #6813 (blue) as shown in the left panel. The percentage inhibition in each assay was calculated and plotted in the right panel. Staurosporine is a nonspecific kinase inhibitor and induces cellular apoptosis.
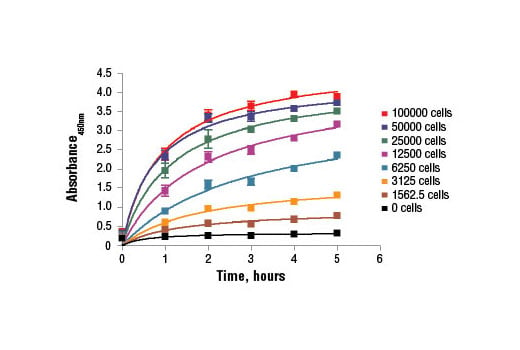
Figure 1. C2C12 cells were seeded at varying density in a 96-well plate and incubated overnight. The XTT assay solution was added to the plate and cells were incubated. The absorbance at 450 nm was measured at 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and 5.0 hours.
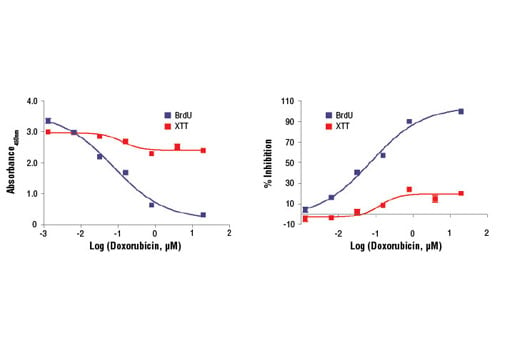
Figure 2. C2C12 cells were seeded at 2x104 cells/well in a 96-well plate and incubated overnight. Cells were then treated with various concentrations of doxorubicin overnight. The cytotoxicity was measured using XTT Cell Viability Kit (red) and BrdU Cell Proliferation Assay Kit #6813 (blue) as shown in the left panel. The percentage inhibition in each assay was calculated and plotted in the right panel. Doxorubicin treatment can lead to cell DNA damage followed by cell cycle arrest.